575: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Internal Pics) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
Tek 575 top.jpg | Tek 575 top.jpg | ||
Tek 575 internal.jpg | Tek 575 internal.jpg | ||
Tek 575 Side.jpg | Internal Side View | |||
Tek 575 rear.jpg | Tek 575 rear.jpg | ||
Tek 575 bottom.jpg | Bottom | Tek_575_Underside.jpg | Bottom#1 | ||
Tek 575 bottom.jpg | Bottom#2 | |||
Tek 575 bottom rear.jpg | Bottom Rear | Tek 575 bottom rear.jpg | Bottom Rear | ||
Tek_575_Chart.png | 575 Load Resistance Chart | Tek_575_Chart.png | 575 Load Resistance Chart | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 14 September 2018
The Tektronix 575 is a curve tracer for transistors, introduced in March 1957. It can be thought of as being composed of three modules: an X-Y display, a step source, and a collector sweep source.
Key Specifications
| Collector Sweep | 0−200 V minimum peak with 1 A current curves, 0−20 V minimum peak with 20 A current curves |
|---|---|
| Vertical Display | plots collector current from 0.01 mA/div to 1 A/div ±3% in 16 Steps |
| Vertical Display | plots base voltage from 0.01 V/div to 0.5 V/div ±3% in 6 Steps |
| Horizontal Display | plots collector voltage from 0.01 V/div to 20 V/div ±3% in 11 Steps |
| Horizontal Display | plots base voltage from 0.01 V/div to 0.5 V/div ±3% in 6 Steps |
| CRT | T52P, P1 phosphor, P2/P7/P11 on request ; 4.2 kV acceleration |
| Line voltage | 105−125 V or 210−250 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz |
| Power | 200 W in standby, 400 W max − Actual consumption based on transistor being tested |
| Size | (W/L/H) 13" × 24" × 16¾" |
| Weight | ~30 kg (70 lb) |
| Cooling | AC Fan |
| Construction | Aluminum alloy chassis, anodized front panel, blue vinyl coated cabinet |
History
While I was working on the 540 series vertical amplifier, Virgil Briton, whose bench was next to me, had put together a vacuum tube curve tracer using stepping relays and other mechanical devices. I remember thinking that, that was a neat display even if it did a lot clicking and was slow. After putting the cross hatch generator together, I knew it would be very easy to do the curve tracer electronically,it started for in house use,but after putting a self-contained instrument together, Tek decided to call it 575 and sell it.
Internals
X-Y display
The vertical and horizontal amplifiers are very similar, using the two halves of a 6CG7 dual-triode tube as the output amplifier. The CRT has −1700 V on the cathode and +2500 V on the anode. The HV power supply uses two 5642 rectifier tubes.
It is possible to use the 575 as an X-Y monitor. The vertical and horizontal range switches have settings for external input, at 0.1 V/div sensitivity.
Step Source
This uses a gated Miller integrator to generate controlled steps. The result is a staircase waveform, which generates different traces in the the family of I-V curves of the transistor.
Power Supplies
The 575 contains three separate power supplies:
- Main Power Supply using T601 (120-095 and, later, 120-0095-01),
supplying power to the amplifiers and step generator in the 575
- High-voltage, using T801, supplying the CRT voltages, +2300 V for the CRT anode and -1700 V for the CRT cathode
- Collector sweep, using T701 (a variac) and T702, supplying the collector current to the device under test
Collector Sweep
Power from the mains goes through an isolation transformer and a variac and is rectified by germanium diodes to produce the collector sweep voltage. The isolation transformer has two pairs of secondary taps, one for high voltage (0 to 200 V) and low current, the other for low voltage (0 to 20 V) and high current. The maximum power that can be delivered to the transistor in either mode is approximately 200 Watts.
575 with Mod 122C has extended collector sweep voltage to 400 V.
Rectifiers
Early 575 versions used selenium rectifiers. A kit for conversion to silicon diodes was available and is documented in the back of the manual.
The 575 has a thermal cutoff.
Type 175 High Current Adaptor

The 575 can be paired with a 175 for high current device measurements.
Links
- "A Power Curve Tracer At Surplus Prices" by Dennis L. Feucht (PDF)
- Some Transistor Measurements Using the Type 575
- Tek 575 @ oscilloscopemuseum.com
Pictures
-
575 w/o Mod 122C
-
575 w Mod 122C
-
-
-
575 Test Panel
-
-
-
575 In a Cart
-
-
575 testing a tunnel diode
-
-
-
Internal Side View
-
-
Bottom#1
-
Bottom#2
-
Bottom Rear
-
575 Load Resistance Chart
-
High-Voltage Power Supply
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
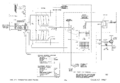
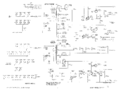
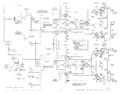
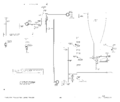
Schematics
-
Unmodified Collector Supply
-
Collector Supply Rectifier with MOD122C
-
Main Power Supply
-
Step Generator
-
Amplifiers
-
CRT Circuit