TNC connector: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "File: tnc-male-crimp-connector.jpg The '''TNC (Threaded Neill–Concelman)''' connector is a threaded version of the BNC connector. The interface specifications for t...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: tnc- | [[File: tnc-female-bulkhead-connector.jpg|250px|right|"Female" TNC connector]] | ||
The '''[[wikipedia:TNC_connector|TNC (Threaded Neill–Concelman) connector]]''' is a threaded version of the [[BNC connector]]. The interface specifications for the TNC and many other connectors are referenced in MIL-STD-348. The connector has a 50 Ω impedance and operates best in the 0–11 GHz frequency spectrum. It has better performance than the [[BNC connector]] at microwave frequencies. Invented in the late 1950s and named after [[wikipedia:Paul Neill|Paul Neill]] of [[wikipedia:Bell Labs|Bell Labs]] and [[wikipedia:Carl Concelman|Carl Concelman]] of [[wikipedia:Amphenol|Amphenol]], the TNC connector has been employed in a wide range of radio and wired applications. | |||
The abbreviation TNC is sometimes incorrectly given as standing for "Threaded Navy Connector". | |||
The abbreviation TNC is sometimes given as standing for Threaded Navy Connector. | |||
The TNC connector features a 7/16"-28 thread. | The TNC connector features a 7/16"-28 thread. | ||
The TNC connector is seen on the External Mixer connector for Tektronix spectrum analyzers like the 2794. | The TNC connector is seen on the External Mixer connector for Tektronix spectrum analyzers like the [[2794]]. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
tnc-male-crimp-connector.jpg | "Male" TNC plug | tnc-male-crimp-connector.jpg | "Male" TNC plug | ||
tnc-female-bulkhead-connector.jpg | "Female" TNC jack | tnc-female-bulkhead-connector.jpg | "Female" TNC jack | ||
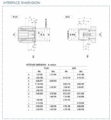
tnc-interface-mechanical.gif | Mechanical | tnc-interface-mechanical.gif | Mechanical drawing | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:Coaxial connectors]] | [[Category:Coaxial connectors]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:19, 27 June 2019

The TNC (Threaded Neill–Concelman) connector is a threaded version of the BNC connector. The interface specifications for the TNC and many other connectors are referenced in MIL-STD-348. The connector has a 50 Ω impedance and operates best in the 0–11 GHz frequency spectrum. It has better performance than the BNC connector at microwave frequencies. Invented in the late 1950s and named after Paul Neill of Bell Labs and Carl Concelman of Amphenol, the TNC connector has been employed in a wide range of radio and wired applications.
The abbreviation TNC is sometimes incorrectly given as standing for "Threaded Navy Connector". The TNC connector features a 7/16"-28 thread.
The TNC connector is seen on the External Mixer connector for Tektronix spectrum analyzers like the 2794.
-
"Male" TNC plug
-
"Female" TNC jack
-
Mechanical drawing