555: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
* [http://bama.edebris.com/manuals/tek/555 555 manual on BAMA] | * [http://bama.edebris.com/manuals/tek/555 555 manual on BAMA] | ||
* [http://w140.com/tek_555_crt.pdf 555 CRT Specs (PDF)] | * [http://w140.com/tek_555_crt.pdf 555 CRT Specs (PDF)] | ||
* [http://w140.com/tek_fcp/tek_555_fac_cal.pdf 555 Factory Calibration | * [http://w140.com/tek_fcp/tek_555_fac_cal.pdf 555 Factory Calibration Procedure (PDF)] | ||
* [http://w140.com/tek_fcp/tek_type_21_and_22_factory_cal_proc.pdf Type 21 and 22 Factory Calibration Procedure (PDF)] | |||
Revision as of 05:46, 7 July 2012
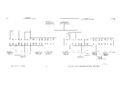
The 555 is a dual-beam CRT oscilloscope introduced by Tektronix in 1959 and made until the late 1960's, when it was replaced by the 556. The system is split across two pieces: the main indicator unit and the external power supply unit. The power supply unit contains the main transformer, rectifiers and regulators for all of the voltages except the filament and CRT HV supplies. The filament and CRT HV voltages are generated in the 555 indicator unit.
The 555 takes two letter-series or 1-series vertical plug-ins
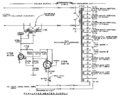
The 555 uses special horizontal plug-ins that contain the trigger and sweep. Early instances of the 555 came with the 21 and 22 horizontal plug-ins. Later instances came with the 21A and 22A horizontal plug-ins, which use tunnel diodes for triggering. Delayed triggering is supported. Since the 555 is a dual-beam scope, it is also possible to start one of the sweeps while the other beam is sweeping. The upper-beam sweep and lower-beam sweeps are, in fact, totally independent.
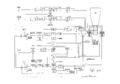
Regulation of the filament supply happens as follows: There is a feedback loop that is formed between the indicator unit and the power supply unit. The power supply sends AC through the interconnection cable to the indicator unit, where it is connected to the primary of the filament transformer. A sample of the output of the filament transformer is sent back through the interconnection cable from the indicator unit to the power supply unit. This performs two functions. First, the filament voltage that is sent back to the power supply unit is used to heat the cathodes of tubes in the power supply unit. Second, this filament voltage is the feedback signal to a regulator in the power supply unit that controls how much voltage is sent to the filament transformer. One of the consequences of this scheme is that it is impossible to energize the power supply unit without the indicator unit connected. The regulator tubes in the power supply would remain cold without filament power, and would not pass any current.
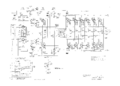
The 555 has a six-section differential distributed vertical output amplifier made of 6DK6 tubes. It is the same as the vertical output amplifier in the 551 and the 545A. An L-C delay line is between the vertical output amplifier and the CRT vertical deflection plates for each channel.
Architecturally, the 555, with its four plug-ins, is similar to the 7844.
- 555 manual on BAMA
- 555 CRT Specs (PDF)
- 555 Factory Calibration Procedure (PDF)
- Type 21 and 22 Factory Calibration Procedure (PDF)
-
-
front view: two timing plug-ins on top and two vertical plug-ins on bottom
-
external power supply
-
left side view
-
right side view
-
top view
-
555 with P11-option
-
Power interconnect
-
Power interconnect
-
Power interconnect
-
timebase interconnect
-
555 block diagram
-
lower beam vertical amplifier
-
power interconnect
-
heater regulator
-
Type 21 trigger
-
block diagram
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT