Phosphor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In a context of chemistry, or when referring to [[ | In a context of chemistry, or when referring to [[cathode-ray tube]]s, '''phosphor''' refers to any of various compounds of transition metals or of rare earths that exhibits phosphorescence. This is not to be confused with the chemical element ''phosphorus'' (symbol P, atomic number of 15). | ||
The choice of phosphor for a CRT is based on the intended application of the instrument. The phosphor affects: | The choice of phosphor for a CRT is based on the intended application of the instrument. The phosphor affects: | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 12 April 2017
In a context of chemistry, or when referring to cathode-ray tubes, phosphor refers to any of various compounds of transition metals or of rare earths that exhibits phosphorescence. This is not to be confused with the chemical element phosphorus (symbol P, atomic number of 15).
The choice of phosphor for a CRT is based on the intended application of the instrument. The phosphor affects:
- trace color
- maximum trace brightness
- trace width
- persistence time
- writing rate
- resistance to burns
Further reading
- http://www.bunkerofdoom.com/tubes/crt/crt_phosphor_research.pdf
- Tektronix Circuit Concepts: Cathode Ray Tubes (see chapters 9 through 16)
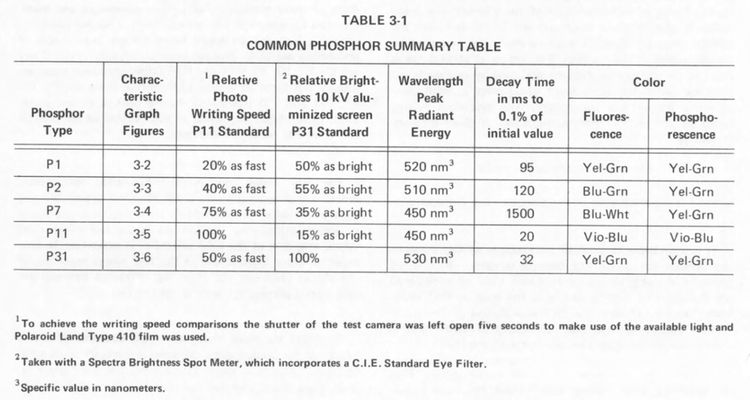
- C50 series camera manual, pages 3-1 to 3-7 - detailed data on P1, P2, P7, P11 and P31 phosphors