7912: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
image=Tek-7912ad.jpg| | image=Tek-7912ad.jpg| | ||
caption=Tektronix 7912AD with [[7A26]] and [[7B90P]] | | caption=Tektronix 7912AD with [[7A26]] and [[7B90P]] | | ||
introduced= | introduced=1974 | | ||
discontinued=1989 | | discontinued=1989 | | ||
summary=500/750 MHz Digitizer| | summary=500/750 MHz Digitizer| | ||
manuals= | manuals= | ||
* [http:// | * [http://w140.com/7912ad_theory.pdf 7912AD Theory] | ||
* [http://w140.com/tek_7912_and_related_digitizer_docs.pdf 7912 and related digitizer documents] | |||
* [http://w140.com/7912ad_reading_gun_supply.pdf 7912AD Reading Gun Supply] | |||
* [http://w140.com/7912ad_writing_gun_supply.pdf 7912AD Writing Gun Supply] | |||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tektronix 7912''' | The '''Tektronix 7912''' was a series of high-speed digitizers that take one [[7000-series_plug-ins#Vertical plug-ins|7000-series vertical plug-in]] and one [[7000-series_plug-ins#Horizontal plug-ins|7000-series horizontal plug-in]]. | ||
All 7912 models use the same internal CRT-based, digitizing [[scan converter]] tube ([[T7912]]) that is not visible from the outside. | |||
The signal from the vertical plug-in deflects a writing beam through [[distributed deflection plates]]. The electrons hit a small flat rectangular solid state target, conceptually similar to that in a digital camera. The resolution of the target is 512×512, giving 512 points in the time domain and 9-bit linear quantization of the input voltage. | |||
With a 7B92 sweeping the whole X-axis in 5 ns, and the 7912AD capturing 512 samples in that sweep, the 7912 performs the function of a 100 GSample/s ADC. | |||
==R7912== | |||
The '''R7912''', introduced in 1974, had a proprietary digital interface. A card for interfacing to a DEC PDP-11 was available. | |||
The Tektronix WP2000 (067-0679-00) Digital Display Controller is an external module that interfaces with the 7912. | |||
Tek also offered configurations with multiple R7912s on a common controller within the WP2000 series. | |||
The R7912 used the [[7000 series readout system]] writing readout characters onto the storage target, which would become part of the output signal in the NON STORE mode. | |||
==7912AD and 7912HB== | |||
From the '''7912AD''' (1978) on, the instrument had a standard [[GPIB interface]]. The 7912AD has 500 MHz bandwidth. It was succeeded by the 750 MHz 7912HB in 1987. | |||
For the 7912AD and 7912HB, special GPIB-controllable plug-in modules with a 'P' suffix, meaning Programmable, were available, e.g. [[7A16P]], [[7A29P]] and [[7B90P]]. | |||
==Internals== | |||
The signal goes from the vertical plug-in to the vertical amplifier to the digitizing tube where it deflects a beam of electrons. | |||
The trace is read from the target by electronics in the 7912AD, digitized, and stored in memory. | The trace is read from the target by electronics in the 7912AD, digitized, and stored in memory. | ||
The reading of the target is asynchronous | The reading of the target is asynchronous to the sweep and therefore the tube can be considered a form of scan converter. | ||
a form of scan converter. Three output methods are provided: NTSC-out, X-Y low-speed analog, | |||
and a [[GPIB interface]]. | Three output methods are provided: NTSC-out, X-Y low-speed analog, and a [[GPIB interface]]. | ||
Bypassing the vertical amplifier, the 7912 can provide a | |||
bandwidth of 1 GHz with a sensitivity of 4 V/Div. | bandwidth of 1 GHz with a sensitivity of 4 V/Div. | ||
With aftermarket modifications to the electronics, 7912AD bandwidths have been extended | With aftermarket modifications to the electronics, 7912AD bandwidths have been extended up to 3 GHz in special cases. | ||
The technology was designed at Tektronix in the 1970's and sold through the 1980's. They were expensive. | The technology was designed at Tektronix in the 1970's and sold through the 1980's. They were expensive. | ||
==Specifications== | ==Specifications== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 52: | ||
The Tektronix 7912AD is 19" wide, 7" tall, 27" deep, and weighs 55 pounds. It uses 360 watts maximum. | The Tektronix 7912AD is 19" wide, 7" tall, 27" deep, and weighs 55 pounds. It uses 360 watts maximum. | ||
== | ==Literature and Software== | ||
* | * [http://w140.com/kurt/7912_gpib_examples.zip 7912 GPIB examples] | ||
* [http://www.scottpages.net/MESCthesis.pdf Thesis on "7912ADM" upgrade version] | |||
* [http://w140.com/US3748585.pdf US Patent 3748585: Silicon Diode Array Scan Converter Tube and Method of Operation. Culter et al. July 1973.] | |||
* | * http://pwww.lle.rochester.edu/media/publications/lle_review/documents/v25/25_Review.pdf LLE Review, Oct-Dec 1985] mentioning the '''LM7912A''', a Lockheed-modified R7912 variant having "a bandwidth of 3.5 GHz at the -3dB point, less than 5% undershoot and overshoot, with a 12-bit output (2 mV/bit)" | ||
* http://w140.com/US3748585.pdf | |||
* http://pwww.lle.rochester.edu/media/publications/lle_review/documents/v25/25_Review.pdf | |||
* http://www.iaea.org/inis/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/10/434/10434659.pdf | * http://www.iaea.org/inis/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/10/434/10434659.pdf | ||
* http://w140.com/boyer_data_acq_ebeam_fus_acc.pdf | * http://w140.com/boyer_data_acq_ebeam_fus_acc.pdf William B. Boyer, DATA ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING ON ELECTRON BEAM FUSION ACCELERATORS. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science Vol.NS-25, No. 1, February 1978] | ||
<!-- * http://130.226.56.153/rispubl/reports_INIS/RISOM2873.pdf no longer available? --> | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* [[Carlo Infante]]: A New Way to Look At Transients (R7912). In [[Media:Tekscope 1973 V5 N6 Nov 1973.pdf | TekScope Vol. 5 No. 6, Nov-Dec 1973]] | |||
* [http://www.radiomuseum.org/forum/tektronix_r7912_transient_digitizer.html Tek R7912 @ radiomuseum.org] | |||
* [[Dale Aufrecht]]: An Intelligent, Programmable Transient Digitizer (7912AD). In [[Media:Tekscope 1979 V11 N1.pdf | TekScope Vol. 11 No. 1, 1979]] | * [[Dale Aufrecht]]: An Intelligent, Programmable Transient Digitizer (7912AD). In [[Media:Tekscope 1979 V11 N1.pdf | TekScope Vol. 11 No. 1, 1979]] | ||
* [http://www.radiomuseum.org/r/tektronix_7912ad.html Tek 7912AD @ radiomuseum.org] | * [http://www.radiomuseum.org/r/tektronix_7912ad.html Tek 7912AD @ radiomuseum.org] | ||
| Line 66: | Line 75: | ||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
===R7912=== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
USA Tek R7912 FrontWork.jpg | R7912 connected to a modern video monitor | |||
R7912 1.jpg | R7912 front | R7912 1.jpg | R7912 front | ||
R7912 2.jpg | R7912 controls | R7912 2.jpg | R7912 controls | ||
R7912 3.jpg | R7912 rear | R7912 3.jpg | R7912 rear | ||
</gallery> | |||
===7912AD=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
7912ad tube.gif | 7912AD digitizer tube | |||
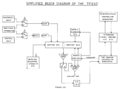
7912ad-block.png | 7912AD block diagram | |||
7912ad.jpg|7912AD front | 7912ad.jpg|7912AD front | ||
Tek wp2000 1.jpg|WP 2000 | Tek wp2000 1.jpg|WP 2000 | ||
Revision as of 08:15, 28 February 2017
The Tektronix 7912 was a series of high-speed digitizers that take one 7000-series vertical plug-in and one 7000-series horizontal plug-in.
All 7912 models use the same internal CRT-based, digitizing scan converter tube (T7912) that is not visible from the outside. The signal from the vertical plug-in deflects a writing beam through distributed deflection plates. The electrons hit a small flat rectangular solid state target, conceptually similar to that in a digital camera. The resolution of the target is 512×512, giving 512 points in the time domain and 9-bit linear quantization of the input voltage.
With a 7B92 sweeping the whole X-axis in 5 ns, and the 7912AD capturing 512 samples in that sweep, the 7912 performs the function of a 100 GSample/s ADC.
R7912
The R7912, introduced in 1974, had a proprietary digital interface. A card for interfacing to a DEC PDP-11 was available. The Tektronix WP2000 (067-0679-00) Digital Display Controller is an external module that interfaces with the 7912. Tek also offered configurations with multiple R7912s on a common controller within the WP2000 series.
The R7912 used the 7000 series readout system writing readout characters onto the storage target, which would become part of the output signal in the NON STORE mode.
7912AD and 7912HB
From the 7912AD (1978) on, the instrument had a standard GPIB interface. The 7912AD has 500 MHz bandwidth. It was succeeded by the 750 MHz 7912HB in 1987.
For the 7912AD and 7912HB, special GPIB-controllable plug-in modules with a 'P' suffix, meaning Programmable, were available, e.g. 7A16P, 7A29P and 7B90P.
Internals
The signal goes from the vertical plug-in to the vertical amplifier to the digitizing tube where it deflects a beam of electrons.
The trace is read from the target by electronics in the 7912AD, digitized, and stored in memory. The reading of the target is asynchronous to the sweep and therefore the tube can be considered a form of scan converter.
Three output methods are provided: NTSC-out, X-Y low-speed analog, and a GPIB interface.
Bypassing the vertical amplifier, the 7912 can provide a
bandwidth of 1 GHz with a sensitivity of 4 V/Div.
With aftermarket modifications to the electronics, 7912AD bandwidths have been extended up to 3 GHz in special cases.
The technology was designed at Tektronix in the 1970's and sold through the 1980's. They were expensive.
Specifications
The Tektronix 7912AD is 19" wide, 7" tall, 27" deep, and weighs 55 pounds. It uses 360 watts maximum.
Literature and Software
- 7912 GPIB examples
- Thesis on "7912ADM" upgrade version
- US Patent 3748585: Silicon Diode Array Scan Converter Tube and Method of Operation. Culter et al. July 1973.
- http://pwww.lle.rochester.edu/media/publications/lle_review/documents/v25/25_Review.pdf LLE Review, Oct-Dec 1985] mentioning the LM7912A, a Lockheed-modified R7912 variant having "a bandwidth of 3.5 GHz at the -3dB point, less than 5% undershoot and overshoot, with a 12-bit output (2 mV/bit)"
- http://www.iaea.org/inis/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/10/434/10434659.pdf
- http://w140.com/boyer_data_acq_ebeam_fus_acc.pdf William B. Boyer, DATA ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING ON ELECTRON BEAM FUSION ACCELERATORS. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science Vol.NS-25, No. 1, February 1978]
Links
- Carlo Infante: A New Way to Look At Transients (R7912). In TekScope Vol. 5 No. 6, Nov-Dec 1973
- Tek R7912 @ radiomuseum.org
- Dale Aufrecht: An Intelligent, Programmable Transient Digitizer (7912AD). In TekScope Vol. 11 No. 1, 1979
- Tek 7912AD @ radiomuseum.org
See Also
Pictures
R7912
-
R7912 connected to a modern video monitor
-
R7912 front
-
R7912 controls
-
R7912 rear
7912AD
-
7912AD digitizer tube
-
7912AD block diagram
-
7912AD front
-
WP 2000
-
WP 2000
-
WP 2000
-
7912AD TV output on NTSC monitor
-
7912AD IEEE 488
-
7912AD IEEE 488
-
7912AD MPU
-
7912AD MPU
-
7912AD 5156
-
7912AD 5156
-
7912AD data buffer
-
7912AD data buffer
-
7912AD translator
-
7912AD translator
-
7912AD graticule generator
-
7912AD graticule generator
-
7912AD X-Y ramp generator
-
7912AD X-Y ramp generator
-
7912AD video processor
-
7912AD 4377
-
7912AD horizontal
-
7912AD scan amplifier