3B1: Difference between revisions
m (→top: clean up, replaced: title=Tektronix → manufacturer=Tektronix |series=560-series scopes |type=, {{Plugin Sidebar 2 → {{Plugin Sidebar, series=560-series scopes → designers=) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
designers= | | designers= | | ||
manuals= | manuals= | ||
* [ | * [[Media:070-344.pdf|Tektronix 3B1 Manual]] (PDF) | ||
* [[Media:070-449.pdf|Tektronix 3B1 Performance Check Out]] | * [[Media:070-449.pdf|Tektronix 3B1 Performance Check Out]] | ||
* [[Media:050-0582-00-TEK_3B1-3B3-MOD.pdf|050-0582-00 Germanium Transistor Replacement]] | * [[Media:050-0582-00-TEK_3B1-3B3-MOD.pdf|050-0582-00 Germanium Transistor Replacement]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
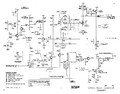
The 3B1 uses vacuum tubes, bipolar junction transistors, and [[tunnel diodes]]. | The 3B1 uses vacuum tubes, bipolar junction transistors, and [[tunnel diodes]]. | ||
The trigger input goes through the int/ext switch and then the | The trigger input goes through the int/ext switch and then the AC/DC coupling switch, and then a [[7895]] cathode follower. | ||
switch, and then a [[7895]] cathode follower. | The output of the cathode follower drives one base of a [[2N2207]] PNP differential amplifier which has a tunnel diode in the collector load. | ||
drives one base of a [[2N2207]] PNP differential amplifier which has a tunnel diode | The tunnel diode generates pulses when it switches back and forth between its two stable voltages, which are capacitively coupled to a [[2N2501]] NPN common emitter amplifier. | ||
in the collector load. The tunnel diode generates pulses when it switches back | |||
and forth between its two stable voltages, which are capacitively coupled to a | |||
[[2N2501]] NPN common emitter amplifier. | |||
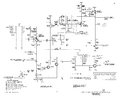
The delay pickoff circuit is a [[6DJ8]] differential amplifier that | The delay pickoff circuit is a [[6DJ8]] differential amplifier that compares the sweep ramp voltage with a knob-controlled DC voltage which determines the point where the delayed trigger starts. | ||
compares the sweep ramp voltage with a knob-controlled | The DC voltage is made by a [[ZZ1000]] 80 V reference passed through a potentiometer-variable voltage divider. | ||
DC voltage which determines the point where the delayed trigger starts. | |||
The DC voltage is made by a [[ZZ1000]] 80 V reference passed through | |||
a potentiometer-variable voltage divider. | |||
When the sweep ramp exceeds the control voltage, a 2.2 mA tunnel diode in the | When the sweep ramp exceeds the control voltage, a 2.2 mA tunnel diode in the plate load of the differential amplifier switches state. | ||
plate load of the differential amplifier switches state. | |||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 20 August 2021
The Tektronix 3B1 is a time-base plug-in introduced in 1962 for 560-series scopes. 10 MHz is is the maximum trigger frequency. The calibrated sweep rates go from 1 s/Div to 500 ns/Div.
There is a switch that enables 5 × horizontal magnification, which makes the fastest sweep 100 ns/Div. The 3B1 has a delayed sweep and a regular sweep.
Key Specifications
- please add
Internals
The 3B1 uses vacuum tubes, bipolar junction transistors, and tunnel diodes.
The trigger input goes through the int/ext switch and then the AC/DC coupling switch, and then a 7895 cathode follower. The output of the cathode follower drives one base of a 2N2207 PNP differential amplifier which has a tunnel diode in the collector load. The tunnel diode generates pulses when it switches back and forth between its two stable voltages, which are capacitively coupled to a 2N2501 NPN common emitter amplifier.
The delay pickoff circuit is a 6DJ8 differential amplifier that compares the sweep ramp voltage with a knob-controlled DC voltage which determines the point where the delayed trigger starts. The DC voltage is made by a ZZ1000 80 V reference passed through a potentiometer-variable voltage divider.
When the sweep ramp exceeds the control voltage, a 2.2 mA tunnel diode in the plate load of the differential amplifier switches state.
Pictures
-
Front
-
Left
-
Right
-
Bottom
-
Top
-
In 1965 Catalog
-
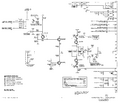
Normal trigger circuit
-
Delayed trigger circuit
-
Delay pickoff circuit
-
Normal sweep circuit
-
Delayed sweep circuit
-
Horizontal amp circuit