507: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
File:Tek_507_heater_wiring.png|Heater Wiring | File:Tek_507_heater_wiring.png|Heater Wiring | ||
File:Tek 507 power supply.png|Power Supply | File:Tek 507 power supply.png|Power Supply | ||
Tek 507 ps 1.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 2.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 3.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 4.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 5.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 6.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 7.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 8.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 9.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 10.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 11.jpg | |||
Tek 507 ps 12.jpg | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:Monolithic tube scopes]] | [[Category:Monolithic tube scopes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 13 November 2016
The Tektronix Type 507 was designed for the power industry for surge testing. It was introduced in 1959.
The scope was intended to operate in an environment of strong electromagnetic fields. It does not take plug-ins. The power supply is external, like in the 517, 551, and 555.
The vertical signal path of the 507 does not contain amplifiers. It has a 5 nanosecond risetime. The input impedance of the 507 is 72 Ω. The maximum sensitivity is deliberately low, at 50 V/cm.
The input attenuator is very unusual for Tek scopes. It is a switch with ten positions in "% of signal", where each step is 10%. The deflection signal is permanently AC-coupled and, unusually, the DC blocking capacitor is after the input attenuator.
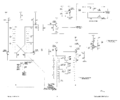
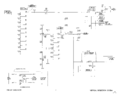
The 507 has 20 kV of post-deflection acceleration, produced by four 1X2 tubes. The lower-voltage power supplies, located in the external box, are all tube except for selenium rectifiers for some of the lower voltages.
Links
- Service Scope No. 18, Feb 1963: Anode-Connector Arcing in the Type 507 Oscilloscope
Pictures
-
507 on Cart
-
507 with Power Supply
-
507 at General Electric
-
Block Diagram
-
Sweep Trigger and Trip Pulse
-
Time Mark Generator
-
Vertical Deflection
-
Horizontal Amplifier
-
CRT Circuit
-
Heater Wiring
-
Power Supply
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-