S-4: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Tek-s-4.jpg | |||
Tek s4.jpg | |||
S4_top.jpg|Top view of the S4 plug-in | |||
S4_left.jpg|Left view | |||
S4_right.jpg|Right view | |||
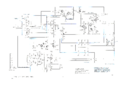
S4 schem.png|Schematic | |||
Tektronix-S4-sampler-board-strobe.jpg|Sampler board, strobe side | |||
Tektronix-S4-sampler-board-preamp.jpg|Sampler board, preamp side | |||
Tektronix-S4-sampler-board-hybrid.jpg|Sampler board, disassembled with parts orientation | |||
Tektronix-S4-hybrid-internal.jpg|Microphotograph of sampler hybrid | |||
Tek s-4 in 7s11.jpg|S-4 in [[7S11]] | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:7000 and 3S series sampling heads]] | [[Category:7000 and 3S series sampling heads]] | ||
Revision as of 08:30, 27 December 2017
Template:Plugin Sidebar 2 The Tektronix S-4 is a sampling head for 7000- and 3S-series samplers. It was designed by George Frye and introduced in 1968. It is the fastest of the S-series plug-in samplers.
Key Specifications
| Rise time | 25 ps (observed with S-50 or S-52, 35 ps) |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 14.5 GHz |
| Input impedance | 50 Ω (terminated SMA connector) |
| Input range | operating, 1 Vp-p; max. safe overload, ±5 V |
| Noise | < 5 mV |
| Features |
|
Internals
The S-4 sampling gate is based upon a traveling wave trapped-charge transmission line in which the sampling window is set by the propagation time of a pulse edge through a thick-film transmission line. This technique requires only a sharp pulse edge rather than a precise pulse width, which is harder to generate. The sampling diodes are housed in a special coaxial connector that provides a high bandwidth signal path.
To disassemble the sampler hybrid, first remove it from the sampler board as per the manual. Remove the input connector using a 7/32" wrench and remove the 20 dB attenuator with small plyers. The ceramic board is held to the housing using roll pins that can be pressed out with a 0.030" pin punch. The hybrid has six diodes, each about 0.75mm square. The cathodes are glued to the gold substrate with conductive epoxy and the anodes are wire-bonded (twice) over a gap to the next step in the strobe line. It appears that a standard beam-lead diode may fit across the gap but cleanly removing a failed diode without damaging the substrate would be quite difficult.
Links
- S-4 page @ amplifier.cd
- James R. Andrews, Comparison of Ultra-Fast Rise Sampling Oscilloscopes. Picosecond Pulse Labs App Note AN-2a, 1989
Pictures
-
-
-
Top view of the S4 plug-in
-
Left view
-
Right view
-
Schematic
-
Sampler board, strobe side
-
Sampler board, preamp side
-
Sampler board, disassembled with parts orientation
-
Microphotograph of sampler hybrid
-
S-4 in 7S11