176: Difference between revisions
(template) |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Plugin Sidebar | {{Plugin Sidebar | ||
|manufacturer=Tektronix | |||
summary=High-current test fixture | | |series=576 | ||
image=Tek-176-3q.jpg | | |type=176 | ||
caption=Tektronix 176 high-current test fixture | | |summary=High-current test fixture | ||
introduced= | |image=Tek-176-3q.jpg | ||
discontinued=(?) | | |caption=Tektronix 176 high-current test fixture | ||
|introduced=1970 | |||
manuals= | |discontinued=(?) | ||
* [ | |designers=Jim Knapton; | ||
* [ | |manuals= | ||
* [[Media:070-1073-00.pdf|Tektronix 176 Manual]] (OCR) | |||
* [[Media:Tek 176 1971 cat.pdf|Tektronix 176 Description in 1971 Catalog]] (OCR) | |||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tektronix 176''' is a pulsed high-current test fixture for the model [[576]] curve tracer. | The '''Tektronix 176''' is a pulsed high-current test fixture for the model [[576]] curve tracer. | ||
The 176 can be considered a more modern replacement for the [[175]]. | The 176 can be considered a more modern replacement for the [[175]]. Both can supply collector currents up to 200 A. | ||
Both can supply collector currents up to 200 A. | |||
The 175 uses a rectified mains-frequency transformer secondary current to supply the collector current to the device under test. | The 175 uses a rectified mains-frequency transformer secondary current to supply the collector current to the device under test. | ||
In contrast, the 176 supplies the collector current by passing stored charge through an SCR. | In contrast, the 176 supplies the collector current by passing stored charge through an SCR. | ||
This pulsed technique allows the 176 to measure points far from the origin of the I-V curve while | This pulsed technique allows the 176 to measure points far from the origin of the I-V curve while keeping the instrument compact and light and the minimizing thermal effects in the device under test. | ||
keeping the instrument compact and light and the minimizing thermal effects in the device under test. | |||
The 175 weighs 84 pounds (38 kg) | The 176 weighs 13 pounds (6 kg), whereas the 175 weighs 84 pounds (38 kg). | ||
The 176 has a cooling fan, as does the 175 (for different reasons). | |||
{{ | {{BeginSpecs}} | ||
{{Spec | Collector Sweep Ranges | | |||
* 15 V / 200 A | |||
* 75 V / 40 A | |||
* 350V / 8 A}} | |||
{{Spec | Power Limits | 1000 W, 100 W, and 10 W}} | |||
{{Spec | Pulse Width | 300 μs, 80 μs}} | |||
{{Spec | Risetime| 80 μs}} | |||
{{Spec | Falltime| 10 μs}} | |||
{{Spec | Vertical Display Collector Current Range | 0.1 μA/division to 20 A/division in 1-2-5 sequence }} | |||
{{Spec | Vertical Display Accuracy 2 A to 20 A| Within 3% of on-screen value}} | |||
{{Spec | Max. Base Current Step Generator Output | 20 A}} | |||
{{EndSpecs}} | |||
==Links== | |||
{{Documents|Link=176}} | |||
{{PatentLinks|176}} | |||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 46: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Tek-176-in-576.jpg | Tek-176-in-576.jpg | ||
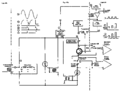
Tek 176 block.png|block diagram | |||
tek_176_1.jpg | |||
tek_176_2.jpg | |||
tek_176_3.jpg | |||
tek_176_4.jpg | |||
tek_176_5.jpg | |||
tek_176_6.jpg | |||
tek_176_7.jpg | |||
tek_176_8.jpg | |||
tek_176_9.jpg | |||
tek_176_10.jpg | |||
Tek-176-3q.jpg | Tek-176-3q.jpg | ||
Tek-176-front.jpg | Tek-176-front.jpg | ||
| Line 39: | Line 65: | ||
[[Category:Introduced in 1971]] | [[Category:Introduced in 1971]] | ||
[[Category:Curve | [[Category:Curve tracer plugins]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:56, 12 July 2024
The Tektronix 176 is a pulsed high-current test fixture for the model 576 curve tracer.
The 176 can be considered a more modern replacement for the 175. Both can supply collector currents up to 200 A.
The 175 uses a rectified mains-frequency transformer secondary current to supply the collector current to the device under test. In contrast, the 176 supplies the collector current by passing stored charge through an SCR. This pulsed technique allows the 176 to measure points far from the origin of the I-V curve while keeping the instrument compact and light and the minimizing thermal effects in the device under test.
The 176 weighs 13 pounds (6 kg), whereas the 175 weighs 84 pounds (38 kg). The 176 has a cooling fan, as does the 175 (for different reasons).
Key Specifications
| Collector Sweep Ranges |
|
|---|---|
| Power Limits | 1000 W, 100 W, and 10 W |
| Pulse Width | 300 μs, 80 μs |
| Risetime | 80 μs |
| Falltime | 10 μs |
| Vertical Display Collector Current Range | 0.1 μA/division to 20 A/division in 1-2-5 sequence |
| Vertical Display Accuracy 2 A to 20 A | Within 3% of on-screen value |
| Max. Base Current Step Generator Output | 20 A |
Links
Documents Referencing 176
| Document | Class | Title | Authors | Year | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekscope 1971 V3 N4 Jul 1971.pdf | Article | Pulsed-Collector High-Current Testing with the 176 | Jim Knapton | 1971 | 176 |
| 48W-3346-3.pdf | Brochure | Making the Correct Semiconductor Measurements Time After Time | 1982 | 576 • 172 • 176 • 577 • 178 • 5CT1N • 7CT1N | |
| 48w-5764.pdf | Brochure | Features Comparison of Tektronix Curve Tracers Versus HP4145A Semiconductor Parameter Analyzer (Tek internal) | Laurie Lawrence | 1984 | 576 • 577 • 176 • 177 • 178 |
Pictures
-
-
block diagram
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-