MOS Technology 6502: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "250px|right|6502AD (click to enlarge) The '''MOS 6502''' is an 8-bit processor that was originally developed by a team led by the engineer Chuck Peddle...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:MOS6502AD.jpg|250px|right|6502AD (click to enlarge)]] | [[File:MOS6502AD.jpg|250px|right|6502AD (click to enlarge)]] | ||
{{Monolithic IC | |||
|Manufacturer=MOS Technology | |||
|Model=6502 | |||
|Part_nos=156-1425-00 | |||
|an=an | |||
|Description=8-bit microprocessor | |||
|Used_in=1220;1225;1230;DC5010; | |||
}} introduced in 1975 that was originally developed by a team led by the engineer Chuck Peddle at MOS Technology (later purchased by Commodore). | |||
It was second-sourced by other companies such as California Micro Devices (GTE Microcircuits), Rockwell, and Synertek. There are several less popular variants, including the 28-pin 6503, [[Rockwell R6504|6504]], 6505, 6506, and 6507 with fewer address pins (4K or 8K address space) and various control signal options. | |||
Western Design Center (WDC) first developed a CMOS version, which is still in production as of 2019. In addition, several implementations (commercial as well as free) are available to synthesize the core into FPGA designs. | |||
The 6502 was a popular choice of processor because of its low price and high capabilities. It was used in multiple early computers such as the Commodore 64, Commodore VIC-20, Apple II, BBC micro, and many others. | |||
==Internals== | ==Internals== | ||
The 6502 had many revisions and derivatives. Most of the revisions have either enhanced | The 6502 had many revisions and derivatives. Most of the revisions have either enhanced its capabilities or have added new features. | ||
Depending on the manufacturer the fabrication process can be CMOS, HMOS and NMOS. | Depending on the manufacturer, the fabrication process can be CMOS, HMOS and NMOS. | ||
The 6502 has three registers, one main register and two index registers. The original MOS 6502 had 151 "legal" opcodes. Later version included more. | |||
{| class="infobox" style="font-size:88%" | |||
|- | |||
|style="text-align:center" |''MOS 6502 registers'' | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
{| style="font-size:88%;" | |||
|- | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>5</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>4</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>3</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>2</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>1</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>1</sup><sub>0</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>9</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>8</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>7</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>6</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>5</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>4</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>3</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>2</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>1</sub> | |||
| style="width:10px; text-align:center;"| <sup>0</sup><sub>0</sub> | |||
| style="width:auto;" | ''(bit position)'' | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="17" | '''Main registers''' | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center; background:white" colspan="8"| | |||
| style="text-align:center;" colspan="8"| A | |||
| style="width:auto; background:white; color:black;"| '''A'''ccumulator | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="17" | '''Index registers''' | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center; background:white" colspan="8"| | |||
| style="text-align:center;" colspan="8"| X | |||
| style="background:white; color:black;"| '''X''' index | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center; background:white" colspan="8"| | |||
| style="text-align:center;" colspan="8"| Y | |||
| style="background:white; color:black;"| '''Y''' index | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center; background:#DDDDDD" colspan="8"| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 | |||
| style="text-align:center;" colspan="8"| SP | |||
| style="background:white; color:black;"| '''S'''tack '''P'''ointer | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="17" | '''Program counter''' | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center;" colspan="16"| PC | |||
| style="background:white; color:black;"| '''P'''rogram '''C'''ounter | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="17" | '''Status register''' | |||
|- style="background:silver;color:black" | |||
| style="text-align:center; background:white" colspan="8" | | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| N | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| V | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| - | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| B | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| D | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| I | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| Z | |||
| style="text-align:center;"| C | |||
| style="background:white; color:black" | '''P''' Processor flags | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
==Used in== | ==Used in== | ||
* [[1230]], [[1225]], [[1220]] | * [[1230]], [[1225]], [[1220]] (65C02) | ||
* [[DC509]], [[DC5009]]: [[Rockwell R6504|R6504]] 28-pin DIP variant (156-1482-00) with 13-bit address bus (8K address space) | |||
* [[DC5010]] | |||
{{Part usage}} | |||
==Supported by== | |||
* [[7D02]] / [[PM101]] | |||
* [[1205]] / [[PM303]] | |||
* [[1220]], [[1225]], [[1230]] / [[PM403]] | |||
* [[1240]], [[1241]] / [[12RM63]] | |||
== | ==Links== | ||
* [http://www.westerndesigncenter.com/wdc/documentation/w65c02s.pdf WDC 65C02 datasheet (Offsite)] | * [http://www.westerndesigncenter.com/wdc/documentation/w65c02s.pdf WDC 65C02 datasheet (Offsite)] | ||
* [http://www.6502.org 6502 information site including datasheets and other derivative processors] | * [http://www.6502.org 6502 information site including datasheets and other derivative processors] | ||
* [[wikipedia:MOS_Technology_6502|Wikipedia: MOS Technology 6502]] | |||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20220629085756if_/http://archive.6502.org/datasheets/mos_6500_mpu_nov_1985.pdf Commodore NMOS 6500 CPU family data sheet, 1985] | |||
==Pictures == | |||
<gallery> | |||
6502diagram.JPG | |||
6502pinout.JPG | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Microprocessors]] | ||
[[Category:Introduced in 1975]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:42, 3 June 2024

The MOS Technology 6502 (P/N 156-1425-00) is an 8-bit microprocessor monolithic integrated circuit introduced in 1975 that was originally developed by a team led by the engineer Chuck Peddle at MOS Technology (later purchased by Commodore).
It was second-sourced by other companies such as California Micro Devices (GTE Microcircuits), Rockwell, and Synertek. There are several less popular variants, including the 28-pin 6503, 6504, 6505, 6506, and 6507 with fewer address pins (4K or 8K address space) and various control signal options.
Western Design Center (WDC) first developed a CMOS version, which is still in production as of 2019. In addition, several implementations (commercial as well as free) are available to synthesize the core into FPGA designs.
The 6502 was a popular choice of processor because of its low price and high capabilities. It was used in multiple early computers such as the Commodore 64, Commodore VIC-20, Apple II, BBC micro, and many others.
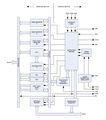
Internals
The 6502 had many revisions and derivatives. Most of the revisions have either enhanced its capabilities or have added new features.
Depending on the manufacturer, the fabrication process can be CMOS, HMOS and NMOS.
The 6502 has three registers, one main register and two index registers. The original MOS 6502 had 151 "legal" opcodes. Later version included more.
| MOS 6502 registers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Used in
- 1230, 1225, 1220 (65C02)
- DC509, DC5009: R6504 28-pin DIP variant (156-1482-00) with 13-bit address bus (8K address space)
- DC5010
Some instruments using part MOS Technology 6502
| Instrument | Manufacturer | Class | Model | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1220 | Tektronix | Logic Analyzer | 1220 | 32 channel logic analyzer | 1988 |
| 1225 | Tektronix | Logic Analyzer | 1225 | 48 channel logic analyzer | 1988 |
| 1230 | Tektronix | Logic Analyzer | 1230 | 16 to 64 channel logic analyzer | 1988 |
| DC5010 | Tektronix | Plug-in | DC5010 | 350 MHz programmable frequency counter | 1982 |
Supported by
Links
- WDC 65C02 datasheet (Offsite)
- 6502 information site including datasheets and other derivative processors
- Wikipedia: MOS Technology 6502
- Commodore NMOS 6500 CPU family data sheet, 1985