7B92A: Difference between revisions
(Removed redirect to 7B92) Tag: Removed redirect |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[https://vintagetek.org/years-at-tektronix-hofer/ According to Bruce Hofer], early 7B92 models exhibited sweep anomalies especially near the start of the sweep, and after trying to fix these he convinced management that a redesign was needed. This resulted in [[Patent US 4009399A]], the [[7B92A]] update, and the [[067-0657-00]] calibration fixture. | [https://vintagetek.org/years-at-tektronix-hofer/ According to Bruce Hofer], early 7B92 models exhibited sweep anomalies especially near the start of the sweep, and after trying to fix these he convinced management that a redesign was needed. This resulted in [[Patent US 4009399A]], the [[7B92A]] update, and the [[067-0657-00]] calibration fixture. | ||
The 7B92A uses one other custom IC, the [[155-0049-00|155-0049-xx]] sweep control circuit. The internal jumper for mainframe selection (7800/7900/7100 vs. slower) | The 7B92A uses one other custom IC, the [[155-0049-00|155-0049-xx]] sweep control circuit. | ||
in parallel with the | The internal jumper (P834/P835) for mainframe selection (7800/7900/7100 vs. slower) | ||
The effect of this jumper is only noticeable for sweep speeds of 20 μs/Div and faster, since | increases the minimum holdoff time on the slower mainframe selection | ||
by adding a 214 pF capacitor, C835, to pin 8 of the sweep control IC (U820) | |||
in parallel with the other capacitors that are selected by the sweep rate switch. | |||
This increases the minimum pulse width of the holdoff signal on [[7000_Series_plug-in_interface|pin B4]] | |||
so that the sweep logic of slower mainframes can handle it properly. | |||
The effect of this jumper is only noticeable for sweep speeds of 20 μs/Div and faster, | |||
since at those sweep speeds the smallest shunt capacitance is used on pin 8, and the holdoff time is minimal. | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 16 May 2023
The Tektronix 7B92A is a 500 MHz dual timebase plug-in for 7000-series scopes. It was introduced 1976, replacing the 7B92. The 7B92A was developed after it was discovered that the 7B92's sweep ramp generator had aberrations in its start-up at the fastest sweep rates.
On the 7B92A, Larson served as the project engineer and worked on the trigger circuits while Bruce Hofer designed the sweep generator, delay pickoff, and output amplifier.
An "HF Sync" triggering mode is provided in which the trigger level control varies the frequency of a built-in oscillator to lock on to the input for input signals from 100 to 500 MHz, providing higher sensitivity than the direct trigger (which is specified up to 500 MHz as well).
As a dual time base, the 7B92A uses the top field in the display readout for the sweep speed of the main and the bottom field for the delayed time base. The delay time can only be read from the 10-turn analog dial.
The 7B92A has no magnifier function but its regular sweep dial setting reaches down to 500 ps/Div. It has no provision for X-Y operation.
Key Specifications
| Sweep speed | 0.5 ns/Div to 0.2 s/Div, 1−2−5 sequence (variable up to 0.5 s/Div) |
|---|---|
| Delay time | 0 to 9.9 Div |
| Triggering | 0.5 Div or 100 mV up to 20 MHz, 1 Div or 500 mV up to 600 MHz |
| Jitter | < 50 ps at 600 MHz |
| Ext Trig input | 1 MΩ // 20 pF or 50 Ω |
Internals
Up to serial number B069999, the 7B92A used a trigger circuit with 155-0061-00 amplifiers and 152-0177-02 tunnel diodes. After that, the 7B92A used a 155-0061-00 trigger amplifier followed by a 155-0150-00 trigger detector.
According to Bruce Hofer, early 7B92 models exhibited sweep anomalies especially near the start of the sweep, and after trying to fix these he convinced management that a redesign was needed. This resulted in Patent US 4009399A, the 7B92A update, and the 067-0657-00 calibration fixture.
The 7B92A uses one other custom IC, the 155-0049-xx sweep control circuit. The internal jumper (P834/P835) for mainframe selection (7800/7900/7100 vs. slower) increases the minimum holdoff time on the slower mainframe selection by adding a 214 pF capacitor, C835, to pin 8 of the sweep control IC (U820) in parallel with the other capacitors that are selected by the sweep rate switch. This increases the minimum pulse width of the holdoff signal on pin B4 so that the sweep logic of slower mainframes can handle it properly. The effect of this jumper is only noticeable for sweep speeds of 20 μs/Div and faster, since at those sweep speeds the smallest shunt capacitance is used on pin 8, and the holdoff time is minimal.
Links
- Zenwizard Studios - Tektronix 7B92A Calibration and Checkin
- Bruce Hofer, My Years at Tektronix
- US Patent 4009399 Gated Ramp Generator
Pictures
-
7B92A front
-
7B92A
-
7B92A right (late S/N, Hypcon-packaged 155-0150-00 trigger detector circuits)
-
7B92A left (late S/N)
-
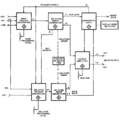
7B92A block diagram
-
A 7B92A (B098xxx) triggering a 974 MHz sine applied to a 7904 mainframe via a 067-0587-02 calibration fixture (maximum triggerable frequency for this specimen).
Custom ICs used in the 7B92A
| Page | Model | Part nos | Description | Designers | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 155-0049-00 | M079G | 155-0049-00 • 155-0049-01 • 155-0049-02 | sweep control with lockout | Bill DeVey | 335 • 464 • 465 • 466 • 475 • 475A • 475M • 485 • 5B31 • 5B40 • 5B52 • 5B42 • 5B44 • 7B53A • 7B80 • 7B85 • 7B87 • 7B92A • 7B90P • 7B10 • 7B15 • SC502 • 7B42N • AN/USM-281C • 067-0657-00 |
| 155-0061-00 | M083 | 155-0061-00 • 155-0061-01 • 155-0061-02 | trigger amplifier | Hans Springer | 7B92 • 7B92A |
| 155-0150-00 | H473 | 155-0150-00 | trigger detector | Walt Ainsworth • Art Metz | 7904A • 7104 • 7B10 • 7B15 • 7B92A • SCD1000 |