7B85: Difference between revisions
Tag: Undo |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|series=7000-series scopes | |series=7000-series scopes | ||
|type=7B85 | |type=7B85 | ||
|summary=400 MHz | |summary=400 MHz delaying timebase | ||
|image=Tek 7b85 front.jpg | |image=Tek 7b85 front.jpg | ||
|caption=Tektronix 7B85 Delaying Timebase plug-in | |caption=Tektronix 7B85 Delaying Timebase plug-in | ||
Revision as of 00:25, 10 March 2023
The Tektronix 7B85 is a 400 MHz delaying timebase for 7000-series scopes with digital delay and delta time read-out capability, typically used in the 7800 Series, e.g. 7844. It does not support X-Y mode.
The delay function differentiates the 7B85 from the otherwise similar 7B80. The 7B87 is also similar to the 7B85 but provides an acquisition clock for a digital storage mainframe instead of a delay.
The 7B85/7B80 combination was introduced in 1976 to replace the 200 MHz 7B71/7B70 that had no digital delay read-out. For the 7104 1 GHz-class scopes, the 7B15/7B10 provide the functionality of 7B85/7B80.
Key Specifications
| Sweep | 5 s/Div to 10 ns/Div in 1-2-5 sequence, ×10 magnifier down to 1 ns/Div, variable to ×2.5 |
|---|---|
| Triggering | to 400 MHz |
| Features |
|
Internals
The 7B85 uses a 155-0185-00 digital voltmeter IC (U686). A ramp generator is started when the trigger signal arrives. The delayed sweep is started when a comparator detects that the ramp has reached a control voltage, set by the front panel knobs on the 7B85. The control voltage is proportional to the amount of delay.
The digital voltmeter in the 7B85 digitizes the control voltage and displays it on the oscilloscope readout, thereby providing the operator with a precise readout of the delay.
Another way of setting up a precisely delayed timebase is to use a 7D11 digital delay module, or even a time mark generator such as the 180A, 181, 184, or 2901.
The 7B85 uses the +50 V supply provided by the mainframe.
Links
- Delta time measurement for the 7000 series. Tekscope Vol.8 No.1, 1976
- Demonstration of delay and delta time measurement on a 7B85
Prices
| Year | 1977 | 1980 | 1984 | 1987 | 1990 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog price | $895 | $1,200 | $1,700 | $1,940 | $2,400 |
| In 2021 Dollars | $4,100 | $4,000 | $4,500 | $4,700 | $5,100 |
Pictures
Hardware
-
Front
-
7B85, left side
-
7B85, left side, delay board removed
-
7B85, right side
-
Family resemblance: 7B15 (top) vs. 7B85 (bottom). Left side.
-
Family resemblance: 7B15 (top) vs. 7B85 (bottom). Right side.
-
Left rear
-
Left front
-
Right front
-
Right rear
Measurements
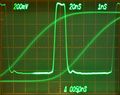
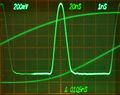
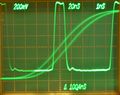
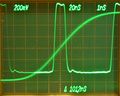
These are examples of measurements with a 7B85 in the Horizontal A and a 7B80 in the Horizontal B compartment (of a 7904).
Horizontal mode is set to alternating to show the pulse signal being triggered (A) and the delayed/magnified part (B).
-
Measuring rise time of a pulse. Delayed signal is scaled for 0-100% on graticule. Delay time is adjusted so the trace crosses the 10% level on the center line. Delta time is adjusted so the delta-delayed trace crosses 90% on the same vertical line. Delta time readout indicates rise time directly.
-
Measuring rise time of a pulse. Same as before, rise time increased to 10 ns (HP8112A generator).
-
Pulse width measurement. Delayed signal and delta-delayed trace cross at 50%. Delta time readout indicates pulse width directly.
-
Pulse period measurement. Delta time is adjusted to overlay the delayed trace with one delayed by an additional period. In this picture, the two traces do not yet overlay exactly.
-
Pulse period measurement. Delayed trace overlays with one delayed by an additional period, delta time reads pulse period.