7S14: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Plugin Sidebar | | {{Plugin Sidebar | ||
manufacturer=Tektronix | type=7S14| | |manufacturer=Tektronix | ||
summary=1 GHz dual-trace, delayed-sweep sampler| | |series=7000-series scopes | ||
image=Tek-7s14-front.jpg| | |type=7S14 | ||
caption=7S14 front| | |summary=1 GHz dual-trace, delayed-sweep sampler | ||
introduced=1974 | | |image=Tek-7s14-front.jpg | ||
discontinued=1988 | |caption=7S14 front | ||
|introduced=1974 | |||
manuals= | |discontinued=1988 | ||
* [[Media:070-1410-00.pdf|Tektronix 7S14 Instruction Manual]] | |manuals= | ||
* [[Media:070-1410-00.pdf|Tektronix 7S14 Instruction Manual]] | |||
** [[Media:070-1410-00 (2).pdf|Alternate]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tektronix 7S14''' is a 1 GHz dual-trace delayed sweep sampler plug-in. | The '''Tektronix 7S14''' is a 1 GHz dual-trace delayed sweep sampler plug-in. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
{{Spec| Sweep rate | 100 µs/Div to 100 ps/Div in 1−2−5 sequence }} | {{Spec| Sweep rate | 100 µs/Div to 100 ps/Div in 1−2−5 sequence }} | ||
{{Spec| Input impedance | 50 Ω }} | {{Spec| Input impedance | 50 Ω }} | ||
{{Spec| Maximum input | {{Spec| Maximum input | 5 V peak }} | ||
{{Spec| Features | | {{Spec| Features | | ||
* Dual channel, CH1 / CH2 / Dual / Add / X−Y modes | * Dual channel, CH1 / CH2 / Dual / Add / X−Y modes | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
The 7S14 has two triggering modes: triggered and HF-sync. | The 7S14 has two triggering modes: triggered and HF-sync. | ||
In triggered mode, the signal passes through two stages of | In triggered mode, the signal passes through two stages of [[MC1672]] ECL logic gate, and then into the [[155-0109]] trigger chip. | ||
[[MC1672]] ECL logic gate, and then into the [[155-0109]] trigger chip. | In HF-sync mode, the 7S14 uses a [[BD4]] back diode (0.1 mA, 3 pF), and inductor, and a [[152-0177-00]] tunnel diode (10 mA, 4 pF) | ||
In HF-sync mode, the 7S14 uses a [[BD4]] back diode (0.1 mA, 3 pF), and inductor, | to form an oscillator that oscillates somewhere between 16.5 MHz and 25 MHz. | ||
and a [[152-0177-00]] tunnel diode (10 mA, 4 pF) to form an oscillator | |||
that oscillates somewhere between 16.5 MHz and 25 MHz. | |||
The sampler used by the 7S14 is a two-diode design. | The sampler used by the 7S14 is a two-diode design. Each of the two input channels has its own sampler. | ||
Each of the two input channels has its own sampler. | |||
The sampling diodes are in CR1A and CR1B of dual diode [[152-0572-00]]. | The sampling diodes are in CR1A and CR1B of dual diode [[152-0572-00]]. | ||
Most boards in the 7S14 and [[5S14N]] are common. However, since [[5000-series plug-ins]] are shorter | Most boards in the 7S14 and [[5S14N]] are common. However, since [[5000-series plug-ins]] are shorter than 7000 series and the [[interfaces|mainframe interface]] is different, | ||
than 7000 series and the [[interfaces|mainframe interface]] is different, the 7S14 contains two 7000-specific interface boards (horizontal/vertical) that plug into the 7000 series mainframe. | the 7S14 contains two 7000-specific interface boards (horizontal/vertical) that plug into the 7000 series mainframe. | ||
The common main horizontal board has the 5000-series interface connector fingers at the rear, these | The common main horizontal board has the 5000-series interface connector fingers at the rear, these remain hidden within the 7S14 ([[Media:Tek-7s14-right.jpg |see photo]]). | ||
remain hidden within the 7S14 ([[Media:Tek-7s14-right.jpg |see photo]]). | |||
==Repair issues== | ==Repair issues== | ||
There are two 1.35 V mercury button cells, BT1 and BT2, in each of the sampler circuits. | There are two 1.35 V mercury button cells, BT1 and BT2, in each of the sampler circuits. | ||
They act as floating bias sources, so if a 7S14 stops working it may be not defective, | They act as floating bias sources, so if a 7S14 stops working it may be not defective, just the batteries are likely to be dead. | ||
just the batteries are likely to be dead. First check the voltage on the cells. | First check the voltage on the cells. The original mercury cells can be replaced with other (less toxic) methods of bias voltage generation. | ||
The original mercury cells can be replaced with other (less toxic) methods of | Two obvious solutions are photovoltaic cells or modern batteries. | ||
bias voltage generation. Two obvious solutions are photovoltaic cells or modern batteries. | |||
The issue has been discussed extensively on the groups.io (formerly Yahoo) TekScopes forum, so search the archives | The issue has been discussed extensively on the groups.io (formerly Yahoo) TekScopes forum, so search the archives | ||
there for more information. Notably, Ed Breya posted [[ | there for more information. Notably, Ed Breya posted [[7S14/Repairs|detailed notes on the 7S14 bias cell issue]]. | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* [ | * [https://www.amplifier.cd/Test_Equipment/Tektronix/Tektronix_7000_series_special/sampler_7S14.htm Tek 7S14 @ amplifier.cd] | ||
* [http://www.barrytech.com/tektronix/tek7000/tek7s14.html Tek 7S14 @ barrytech.com] | * [http://www.barrytech.com/tektronix/tek7000/tek7s14.html Tek 7S14 @ barrytech.com] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 77: | ||
|align=right| $6,490 | |align=right| $6,490 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! In 2023 Dollars | ||
|align=right| $ | |align=right| $11,400 | ||
|align=right| $ | |align=right| $11,800 | ||
|align=right| $ | |align=right| $16,700 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
According to an [[Media:Tek Schottky Diodes Memo rot.pdf|internal memo]], in 1979 annual sales were estimated at 98 units. | |||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
| Line 104: | Line 103: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{{ | ==Components== | ||
{{Parts|7S14}} | |||
[[Category:7000 series combined plugins]] | [[Category:7000 series combined plugins]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:7000 series sampling plugins]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:54, 25 October 2023
The Tektronix 7S14 is a 1 GHz dual-trace delayed sweep sampler plug-in. It is almost identical to the 5S14 plugin for the 5000 series.
It is a complete sampling system unlike, for example, the 7S11, which requires a separate timing plug-in to provide triggering and sampling pulse generation.
Key Specifications
| Rise time | 350 ps (1 GHz bandwidth) |
|---|---|
| Trigger bandwidth | 100 MHz (Norm/Auto trigger), 1 GHz (HF sync) |
| Vertical deflection | 2 mV/Div to 0.5 V/Div in 1−2−5 sequence |
| Sweep rate | 100 µs/Div to 100 ps/Div in 1−2−5 sequence |
| Input impedance | 50 Ω |
| Maximum input | 5 V peak |
| Features |
|
Internals
The 7S14 contains two samplers, trigger and sweep circuitry, and circuitry to interface it with the 7000-series mainframe in which it operates. The mainframe provides the 7S14 with power. The 7S14 sends the mainframe horizontal, vertical and readout signals.
The 7S14 has an integrated delay measurement function.
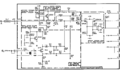
The 7S14 has two triggering modes: triggered and HF-sync. In triggered mode, the signal passes through two stages of MC1672 ECL logic gate, and then into the 155-0109 trigger chip. In HF-sync mode, the 7S14 uses a BD4 back diode (0.1 mA, 3 pF), and inductor, and a 152-0177-00 tunnel diode (10 mA, 4 pF) to form an oscillator that oscillates somewhere between 16.5 MHz and 25 MHz.
The sampler used by the 7S14 is a two-diode design. Each of the two input channels has its own sampler. The sampling diodes are in CR1A and CR1B of dual diode 152-0572-00.
Most boards in the 7S14 and 5S14N are common. However, since 5000-series plug-ins are shorter than 7000 series and the mainframe interface is different, the 7S14 contains two 7000-specific interface boards (horizontal/vertical) that plug into the 7000 series mainframe. The common main horizontal board has the 5000-series interface connector fingers at the rear, these remain hidden within the 7S14 (see photo).
Repair issues
There are two 1.35 V mercury button cells, BT1 and BT2, in each of the sampler circuits. They act as floating bias sources, so if a 7S14 stops working it may be not defective, just the batteries are likely to be dead. First check the voltage on the cells. The original mercury cells can be replaced with other (less toxic) methods of bias voltage generation. Two obvious solutions are photovoltaic cells or modern batteries. The issue has been discussed extensively on the groups.io (formerly Yahoo) TekScopes forum, so search the archives there for more information. Notably, Ed Breya posted detailed notes on the 7S14 bias cell issue.
Links
Prices
| Year | 1974 | 1980 | 1988 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog price | $1,850 | $3,200 | $6,490 |
| In 2023 Dollars | $11,400 | $11,800 | $16,700 |
According to an internal memo, in 1979 annual sales were estimated at 98 units.
Pictures
-
7S14 front panel
-
-
-
-
Left side
-
Right side
-
Sampler boards detail with cover removed
-
Trigger board detail - tunnel diode oscillator (CR220, CR221, L220)
-
Sampler schematic
-
Trigger schematic
-
Modified sampler with head-to-head leds
-