555: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Zenwizard video and tidy links) |
||
| (70 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Oscilloscope Sidebar | | {{Oscilloscope Sidebar | ||
|manufacturer=Tektronix | |||
summary=Dual beam 30 MHz scope | | |series=500-series scopes | ||
image= | |model=555 | ||
caption=Tektronix 555 | |summary=Dual beam 30 MHz scope | ||
introduced=1959 | | |image=Tek_555-wTrace.jpeg | ||
discontinued= | |caption=Tektronix 555 Front | ||
manuals= | |introduced=1959 | ||
* [ | |discontinued=1970 | ||
* [ | |designers= | ||
* [ | |manuals= | ||
* [ | * [[Media:070-165.pdf | 555/21A/22A Manual 070-165]] | ||
* [ | * [[Media:070-403.pdf | 555/21A/22A Manual 070-403]] | ||
* [ | |||
* [ | * [[Media:070-227.pdf | 555 Operator's Handbook]] (bad-OCR) | ||
* [[Media:Tektronix 21a-22a.pdf | 21A and 22A section of 555 manual]] | |||
<small> | |||
'''Alternate copies''' | |||
* [https://bama.edebris.com/manuals/tek/555 @ BAMA] | |||
'''Modifications''' | |||
* [[Media:040-0328-01.pdf | Modification for Additional Trigger Sources]] (bad-OCR) | |||
* [[Media:tek_555_fcp.pdf | 555 Factory Calibration Procedure]] (OCR) | |||
'''Calibration''' | |||
* [[Media:tek_type_21_22_fcp.pdf | Type 21 and 22 Factory Calibration Procedure]] (OCR) | |||
* [[Media:Tek 555 cal outline.pdf | Tektronix 555 Calibration Outline]] | |||
'''Specifications''' | |||
* [[Media:tek_555_crt_specs.pdf | 555 CRT Specs]] (OCR) | |||
'''Other''' | |||
* [[Media:tek_555_section_21a_22a.pdf | 21A and 22A section of 555 manual]] (bad-OCR) | |||
* [[Media:555 compatibility notes.pdf | Notes on the compatibility of 555 plug-ins and mainframe]] | |||
* [https://w140.com/Tektronix_555_dt._Kurzanleitung.pdf German Introduction the 555] (OCR) | |||
</small> | |||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tektronix Type 555''', nicknamed "Triple Nickel", is a [[dual-beam scopes|dual-beam CRT oscilloscope]] introduced by Tektronix in | |||
[[introduced_in_1959|1959]] and made until the late 1960's, when it was replaced by the [[556]]. | |||
The system is split across two cabinets, the main indicator unit and the external power supply unit. | |||
The power supply unit contains the main transformer, rectifiers and regulators for all of the voltages except the filament and CRT HV supplies. | |||
The system is split across two | |||
and the external power supply unit. | |||
The power supply unit contains the main transformer, | |||
rectifiers and regulators for all of the voltages | |||
except the filament and CRT HV supplies. | |||
The filament and CRT HV voltages are generated in the 555 indicator unit. | The filament and CRT HV voltages are generated in the 555 indicator unit. | ||
The Tektronix 555 takes two | The Tektronix 555 takes two [[letter-series and 1-series plug-ins|letter-series or 1-series vertical plug-ins]] | ||
[[letter-series and 1-series plug-ins|letter-series or 1-series vertical plug-ins]] | |||
{{BeginSpecs}} | |||
{{Spec | Bandwidth | DC to 30 MHz, 3 dB down at 30 MHz ±0.5 dB (with [[K|Type K plug-in]]) }} | |||
{{Spec | Rise time | 120 ns}} | |||
{{Spec | External Horizontal Input | 0.2 V/cm to 20 V/cm, DC to 240 kHz }} | |||
{{Spec | Sweep Rates | 100 ns/div to 5 s/div (Type 21 and 22)}} | |||
{{Spec | External Trigger Level | 0.2 V to 10 V}} | |||
{{Spec | Calibrator | ~1 kHz, 200 μV<sub>p-p</sub> to 100 V<sub>p-p</sub>}} | |||
{{Spec | CRT | [[T5550]], 10 kV acceleration, P2 [[phosphor]] standard (P1, P7, P11 optional). Usable area: Total 6 cm, 4 cm per beam, 2 cm overlap between beams }} | |||
{{Spec | Line Voltage | 105 to 125 V or 210 to 250 V, 50/60 Hz}} | |||
{{Spec | Power Consumption | 1050 W}} | |||
{{Spec | Dimensions | Indicator Unit, 24"×13"×20"; Power Supply Unit, 17.5"×13"×10" (LWH)}} | |||
{{Spec | Weight | Indicator Unit, 68 lb; Power Supply, 45 lb}} | |||
{{Spec | Cooling | AC Fan for both Power Supply and Indicator Unit}} | |||
{{EndSpecs}} | |||
== Type 21A and 22A Timebases == | ==Internals== | ||
Later instances came with | === Type 21 and 22 Timebases === | ||
the 21A and 22A horizontal plug-ins, | The 555 uses special horizontal plug-ins that contain the trigger and sweep. | ||
which use [[tunnel diodes]] for triggering. | Early instances of the 555 came with the [[21 (plug-in)|Type 21]] and [[22|Type 22]] horizontal plug-ins. | ||
Type 21 is suggested for the upper beam and type 22 is suggested as the lower beam time base, as type 22 contains delayed trigger, and only the lower beam horizontal section is provided with delayed trigger pickup circuitry. The Delay multiplier control pot is also provided on the lower beam section. | |||
A rigid plug-in extension for the timebases (part number [[013-013]]) was included with every 555. | |||
=== Type 21A and 22A Timebases === | |||
Later instances came with the [[21A]] and [[22A]] horizontal plug-ins, which use [[tunnel diodes]] for triggering. | |||
Delayed triggering is supported. | Delayed triggering is supported. | ||
Since the 555 is a dual-beam scope, it is also possible | |||
to start one of the sweeps while the other beam is sweeping. | Since the 555 is a dual-beam scope, it is also possible to start one of the sweeps while the other beam is sweeping. | ||
The upper-beam sweep and lower-beam sweeps are, in fact, totally independent. | The upper-beam sweep and lower-beam sweeps are, in fact, totally independent. | ||
== Filament Supply Regulator == | === Power Supply and Filament Supply Regulator === | ||
The external power supply unit generates all the B+ Voltages (–150, +100, +225, +330, +350 and +500 V) required by the indicator unit. | |||
These are fed to the indicator unit through the interconnect cable. | |||
There are two transformers inside the power supply unit – one to generate heater voltages (except for the tubes noted below), the other to generate all the B+ plate voltages. | |||
The heater/filament supply for all the tubes inside the indicator unit are generated by a transformer inside the indicator unit. | |||
back through the interconnection cable (part number 012-032) | A saturable inductor, located in the power supply unit, is connected in series with its primary as the control element of an AC regulator circuit. | ||
One 6.3 V winding from the indicator unit filament transformer is fed back through the interconnection cable (part number [[012-032]]) | |||
to supply heaters of specific tubes in the power supply unit (V624, V634, V664, V684, V694). Moreover, a regulator Tube (2AS-15, a Temperature Limited Diode) | |||
is used to sense this filament voltage and derive a control DC current through the saturable inductor, thereby closing the control loop. | |||
One of the consequences of this scheme is that it the power supply unit will not energize the plate voltages (except +100 V) without the indicator unit connected, because | |||
in the power supply unit | * the 12AX7 comparators and 6AU6 error amplifiers are heated from the indicator unit, so the main series pass tubes (6080s and 12B4s) are not driven even though they are heated from a transformer in the power supply unit; | ||
to the | * The primary of the plate voltage transformer inside the power supply unit is looped via the thermal cutout in the indicator unit, i.e. the plate voltage transformer in the power supply will not get power unless the indicator unit is attached. | ||
is | Even if one were to power up the power supply itself by bypassing the thermal cut-out and applying local heater voltages to the tubes normally supplied by the indicator unit, the power supply will not regulate as the design employs shunting resistors across the series pass tubes, and can therefore not regulate without a load. | ||
the indicator | |||
=== Vertical Amplifier === | |||
The Tektronix 555 has a six-section differential [[distributed amplifier|distributed vertical output amplifier]] made of [[6DK6]] tubes. | |||
It is the same as the vertical output amplifier in the [[551]] and the [[545|545A]]. | |||
An L-C [[delay line]] is located between the vertical output amplifier and the CRT vertical deflection plates for each channel. | |||
Twelve 6DK6 tubes per beam are used in the main amplifier. | |||
A pair of [[6DK6]]s are used to pick up the trigger signal from the differential drive, and pass it to the horizontal plug-in via a cathode follower as a single-ended trigger signal. | |||
Another pair of [[6DJ8]]s are used as grid-line driver cathode followers, fed by the [[12BY7]] input driver stage, which takes the differential input from the vertical plug-in. | |||
A pair of triodes out of [[6DJ8]]s are used as amplifier to drive beam position indicator neons near the CRT. | |||
Architecturally, the 555, with its four plug-ins, is similar to the [[7844]]. | |||
=== CRT Circuit === | |||
The CRT circuit in the 555 is really two separate modules. | |||
It is split between two internal metal enclosures, each one containing a high voltage transformer and associated tubes. | |||
The lower beam HV power supply is based on transformer T901 and produces: | |||
* CRT anode voltage: +8,650 V | |||
* lower beam CRT cathode voltage: -1,350 V | |||
* lower beam CRT control grid (blanking) voltage: floating, -1,500 V | |||
The upper beam HV power supply is based on T801 and produces: | |||
The | * upper beam CRT cathode voltage: -1,350 V | ||
* upper beam CRT control grid (blanking) voltage: floating, -1,500 V | |||
Rectification and voltage multiplication is performed by a total of six [[5642]] rectifier tubes. | |||
Each of the two HV power supplies is independently regulated using a two-stage common-cathode amplifier based on a [[12AU7]] dual triode. | |||
The oscillator tube is a [[6CZ5]] power pentode. | |||
The 555 uses the [[T5550]] CRT. | |||
The CRT | |||
==Links== | |||
* | * [https://lazyelectrons.wordpress.com/2019/11/10/tektronix-555-restore/ Tektronix 555 Restore/Repair with Videos at Lazy Electrons Blog ] | ||
* | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BvbNBZX6kNE Tektronix 555 in operation] @ YouTube | ||
* [http://www.barrytech.com/tektronix/vintage/tek555.html Tektronix 555 @ barrytech.com ] | |||
* [http://www.radiomuseum.org/r/tektronix_dual_beam_oscilloscope_55_2.html Tektronix 555 @ radiomuseum.org ] | |||
* [http://www.lemis.com/grog/Albums/Tektronix-555.php Greg's 555] - lots of photos | |||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RjuMm4pQyBI Tektronix 555 Troubleshooting] Zenwizard @ YouTube | |||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Tek 555 front fl2.jpg | |||
Tek 555 front fl.jpg |front view: two timing plug-ins on top and two vertical plug-ins on bottom | |||
Tek 555-CA.jpg | Tek 555 with CA Dual Trace Plug-ins | |||
Tek_555-Delayed-Trace.jpg | Tek 555 in Delayed Trigger Mode | |||
555 P11.JPG | 555 with P11 [[phosphor]] option | |||
555_P7.jpg | 555 with P7 [[phosphor]] option (fast blue / slow green) | |||
Tek 555 1050 1.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 2.jpg | |||
Wellenkino 555-2.jpg | |||
Wellenkino 555.jpg | |||
Tek 555 rear.jpg | 555 rear | |||
Tek 555 rear on cart.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 3.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 4.jpg | |||
Tek 555 side on cart.jpg | |||
Tek 555 with camera.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 5.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 6.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 7.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 8.jpg | |||
Tek 555 technikum29.de.jpg | 555 photo from technikum29.de | |||
Tek 555 rear2.jpeg | |||
Tek 555 power connector.jpeg | |||
</gallery> | |||
'''Internals''' | |||
<gallery> | |||
Tek_555-LHS.jpeg | 555 Internals, left side (upper beam) | |||
Tek_555-RHS.jpeg | 555 Internals, right side (lower beam) | |||
Tek_555_Top.jpg | 555 Top with with HV Cover off | |||
Tek-555-Bottom.jpeg | 555 Bottom | |||
Tek_555_V-Amp.jpg | Vertical Amplifier (Lower Beam) | |||
555_top_int.jpg | top view | |||
555_left_int.jpg | left side view | |||
555_rt_int.jpg | right side view | |||
Tek 555 1050 10.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 9.jpg | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
'''CRT''' | |||
<gallery> | |||
Tek 555 crt1.jpg | CRT | |||
Tek 555 crt2.jpg | CRT | |||
Tek 555 crt3.jpg | CRT | |||
Tek 555 crt4.jpg | CRT | |||
Tek 555 crt5.jpg | CRT | |||
Tek 555 crt6.jpg | CRT | |||
</gallery> | |||
'''Power Supply''' | |||
<gallery> | |||
Tek-555-PS-Front.jpg | 555 Power Supply - Front | |||
Tek-555-PS-Rear.jpg | 555 Power Supply - Rear | |||
555_ps.jpg | External power supply | |||
Tek-555-PS-Top.jpg | 555 Power Supply Internals - Top | |||
Tek-555-PS-Bottom.jpg | 555 Power Supply Internals - Bottom | |||
Tek 555 ps no tubes2.jpg | 555 power supply | |||
Tek 555 ps bottom.png | 555 Power supply | |||
Tek 555 ps no tubes1.png | 555 Power supply | |||
Tek 555 ps no tubes3.png | 555 Power supply | |||
Tek 555 ps no tubes4.png | 555 Power supply | |||
Tek 555 1050 11.jpg | |||
Tek 555 1050 12.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
'''Accessories''' | |||
<gallery> | |||
Tek 013-013.JPG | Timebase plug-in extender, part number [[013-0013-00]] | |||
Tek 555 cable 3.jpg | Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00 | |||
Tek 555 cable 2.jpg | Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00 | |||
Tek 555 cable 1.jpg | Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00 | |||
</gallery> | |||
'''Schematics''' | |||
<gallery> | |||
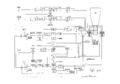
Tek 555 block.png | 555 block diagram | |||
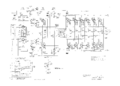
555 lower vert.png | lower beam vertical amplifier | |||
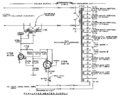
Tek 555 21 trigger.png | Type 21 trigger | |||
Tek_555_block.png | block diagram | |||
Tek 555 crt circuit.png | CRT circuit | |||
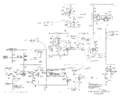
Tek 555 lvreg.png | heater regulator | |||
Tek 555 timebase interconnect3.png | time base interconnect | |||
Tek 555 power interconnect.png | power interconnect | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Components== | |||
{{Parts|555}} | |||
[[Category:500 series scopes]] | [[Category:500 series scopes]] | ||
[[Category:Dual beam scopes]] | [[Category:Dual beam scopes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 18 July 2024
The Tektronix Type 555, nicknamed "Triple Nickel", is a dual-beam CRT oscilloscope introduced by Tektronix in 1959 and made until the late 1960's, when it was replaced by the 556.
The system is split across two cabinets, the main indicator unit and the external power supply unit. The power supply unit contains the main transformer, rectifiers and regulators for all of the voltages except the filament and CRT HV supplies. The filament and CRT HV voltages are generated in the 555 indicator unit.
The Tektronix 555 takes two letter-series or 1-series vertical plug-ins
Key Specifications
| Bandwidth | DC to 30 MHz, 3 dB down at 30 MHz ±0.5 dB (with Type K plug-in) |
|---|---|
| Rise time | 120 ns |
| External Horizontal Input | 0.2 V/cm to 20 V/cm, DC to 240 kHz |
| Sweep Rates | 100 ns/div to 5 s/div (Type 21 and 22) |
| External Trigger Level | 0.2 V to 10 V |
| Calibrator | ~1 kHz, 200 μVp-p to 100 Vp-p |
| CRT | T5550, 10 kV acceleration, P2 phosphor standard (P1, P7, P11 optional). Usable area: Total 6 cm, 4 cm per beam, 2 cm overlap between beams |
| Line Voltage | 105 to 125 V or 210 to 250 V, 50/60 Hz |
| Power Consumption | 1050 W |
| Dimensions | Indicator Unit, 24"×13"×20"; Power Supply Unit, 17.5"×13"×10" (LWH) |
| Weight | Indicator Unit, 68 lb; Power Supply, 45 lb |
| Cooling | AC Fan for both Power Supply and Indicator Unit |
Internals
Type 21 and 22 Timebases
The 555 uses special horizontal plug-ins that contain the trigger and sweep. Early instances of the 555 came with the Type 21 and Type 22 horizontal plug-ins.
Type 21 is suggested for the upper beam and type 22 is suggested as the lower beam time base, as type 22 contains delayed trigger, and only the lower beam horizontal section is provided with delayed trigger pickup circuitry. The Delay multiplier control pot is also provided on the lower beam section.
A rigid plug-in extension for the timebases (part number 013-013) was included with every 555.
Type 21A and 22A Timebases
Later instances came with the 21A and 22A horizontal plug-ins, which use tunnel diodes for triggering. Delayed triggering is supported.
Since the 555 is a dual-beam scope, it is also possible to start one of the sweeps while the other beam is sweeping. The upper-beam sweep and lower-beam sweeps are, in fact, totally independent.
Power Supply and Filament Supply Regulator
The external power supply unit generates all the B+ Voltages (–150, +100, +225, +330, +350 and +500 V) required by the indicator unit. These are fed to the indicator unit through the interconnect cable.
There are two transformers inside the power supply unit – one to generate heater voltages (except for the tubes noted below), the other to generate all the B+ plate voltages.
The heater/filament supply for all the tubes inside the indicator unit are generated by a transformer inside the indicator unit. A saturable inductor, located in the power supply unit, is connected in series with its primary as the control element of an AC regulator circuit. One 6.3 V winding from the indicator unit filament transformer is fed back through the interconnection cable (part number 012-032) to supply heaters of specific tubes in the power supply unit (V624, V634, V664, V684, V694). Moreover, a regulator Tube (2AS-15, a Temperature Limited Diode) is used to sense this filament voltage and derive a control DC current through the saturable inductor, thereby closing the control loop.
One of the consequences of this scheme is that it the power supply unit will not energize the plate voltages (except +100 V) without the indicator unit connected, because
- the 12AX7 comparators and 6AU6 error amplifiers are heated from the indicator unit, so the main series pass tubes (6080s and 12B4s) are not driven even though they are heated from a transformer in the power supply unit;
- The primary of the plate voltage transformer inside the power supply unit is looped via the thermal cutout in the indicator unit, i.e. the plate voltage transformer in the power supply will not get power unless the indicator unit is attached.
Even if one were to power up the power supply itself by bypassing the thermal cut-out and applying local heater voltages to the tubes normally supplied by the indicator unit, the power supply will not regulate as the design employs shunting resistors across the series pass tubes, and can therefore not regulate without a load.
Vertical Amplifier
The Tektronix 555 has a six-section differential distributed vertical output amplifier made of 6DK6 tubes. It is the same as the vertical output amplifier in the 551 and the 545A. An L-C delay line is located between the vertical output amplifier and the CRT vertical deflection plates for each channel.
Twelve 6DK6 tubes per beam are used in the main amplifier. A pair of 6DK6s are used to pick up the trigger signal from the differential drive, and pass it to the horizontal plug-in via a cathode follower as a single-ended trigger signal.
Another pair of 6DJ8s are used as grid-line driver cathode followers, fed by the 12BY7 input driver stage, which takes the differential input from the vertical plug-in. A pair of triodes out of 6DJ8s are used as amplifier to drive beam position indicator neons near the CRT.
Architecturally, the 555, with its four plug-ins, is similar to the 7844.
CRT Circuit
The CRT circuit in the 555 is really two separate modules. It is split between two internal metal enclosures, each one containing a high voltage transformer and associated tubes. The lower beam HV power supply is based on transformer T901 and produces:
- CRT anode voltage: +8,650 V
- lower beam CRT cathode voltage: -1,350 V
- lower beam CRT control grid (blanking) voltage: floating, -1,500 V
The upper beam HV power supply is based on T801 and produces:
- upper beam CRT cathode voltage: -1,350 V
- upper beam CRT control grid (blanking) voltage: floating, -1,500 V
Rectification and voltage multiplication is performed by a total of six 5642 rectifier tubes. Each of the two HV power supplies is independently regulated using a two-stage common-cathode amplifier based on a 12AU7 dual triode. The oscillator tube is a 6CZ5 power pentode.
The 555 uses the T5550 CRT.
Links
- Tektronix 555 Restore/Repair with Videos at Lazy Electrons Blog
- Tektronix 555 in operation @ YouTube
- Tektronix 555 @ barrytech.com
- Tektronix 555 @ radiomuseum.org
- Greg's 555 - lots of photos
- Tektronix 555 Troubleshooting Zenwizard @ YouTube
Pictures
-
-
front view: two timing plug-ins on top and two vertical plug-ins on bottom
-
Tek 555 with CA Dual Trace Plug-ins
-
Tek 555 in Delayed Trigger Mode
-
555 with P11 phosphor option
-
555 with P7 phosphor option (fast blue / slow green)
-
-
-
-
-
555 rear
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
555 photo from technikum29.de
-
-
Internals
-
555 Internals, left side (upper beam)
-
555 Internals, right side (lower beam)
-
555 Top with with HV Cover off
-
555 Bottom
-
Vertical Amplifier (Lower Beam)
-
top view
-
left side view
-
right side view
-
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
-
CRT
Power Supply
-
555 Power Supply - Front
-
555 Power Supply - Rear
-
External power supply
-
555 Power Supply Internals - Top
-
555 Power Supply Internals - Bottom
-
555 power supply
-
555 Power supply
-
555 Power supply
-
555 Power supply
-
555 Power supply
-
-
Accessories
-
Timebase plug-in extender, part number 013-0013-00
-
Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00
-
Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00
-
Power interconnect, part number 012-0032-00
Schematics
-
555 block diagram
-
lower beam vertical amplifier
-
Type 21 trigger
-
block diagram
-
CRT circuit
-
heater regulator
-
time base interconnect
-
power interconnect