503: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
The 503 was $625 in 1960 versus, for example, $1000 for the [[516]] in 1960. | The 503 was $625 in 1960 versus, for example, $1000 for the [[516]] in 1960. | ||
Due to is its low bandwidth, the 503 can operate at high sensitivities while not responding to interference from | The 503 features two identical phase matched amplifiers with true differential inputs. | ||
broadcast transmitter RF fields, making it suitable for biomedical work. | The scope has a bandwidth specification of 450 kHz and sensitivity to 1 mV/cm. | ||
Due to is its low bandwidth, the 503 can operate at high sensitivities while not responding to interference from broadcast transmitter RF fields, making it suitable for biomedical work. | |||
A large market for the 503 was in electronics labs of educational institutions. | A large market for the 503 was in electronics labs of educational institutions. | ||
The differential inputs are useful for entry level students to experiment with observing voltages not referenced to ground. | The differential inputs are useful for entry level students to experiment with observing voltages not referenced to ground. | ||
{{ | {{BeginSpecs}} | ||
{{Spec | Bandwidth | DC to 450 kHz (AC coupled 10 Hz) }} | |||
{{Spec | Deflection | 1 mV/div to 20 V/div, 1–2–5, and 2.5:1 variable }} | |||
{{Spec | Inputs | 1 MΩ // 47 pF; max. 350 V (DC + peak AC) }} | |||
{{Spec | CMRR | 100:1 in 1 mV/div to 200 mV/div, 30:1 above (all at ≤50 kHz) }} | |||
{{Spec | Phase | <1° to 450 kHz in 1 mV/div to 200 mV/div (equal X and Y sensitivity, variable in CAL, like polarities, DC coupling); <2° to 50 kHz in 500 mv/div to 20 V/div) }} | |||
{{Spec | Sweep | 1 μs/div to 5 s/div, 1−2−5, variable 2.5:1, magnifier ×2, ×5, ×10, ×20, ×50 }} | |||
{{Spec | Trigger | Internal, 0.5 div from 50 Hz to 50 kHz, increasing to 2 div at 450 kHz; external 0.5 V from 50 Hz to 450 kHz }} | |||
{{Spec | CRT | [[T5030]], 3 kV (no post-deflection acceleration), P2 [[phosphor]] standard }} | |||
{{EndSpecs}} | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 54: | ||
The 503 is mostly a vacuum tube design with a differential transistor stage following the differential input amplifiers. | The 503 is mostly a vacuum tube design with a differential transistor stage following the differential input amplifiers. | ||
The power supply design is unique in that unlike other scopes where the high frequency transformer only generates the CRT operating voltages, | The power supply design is unique in that unlike other scopes where the high frequency transformer only generates the CRT operating voltages, | ||
Revision as of 02:15, 24 June 2024
The Tektronix Type 503 is a low-cost, low-bandwidth monolithic oscilloscope introduced in 1960 specializing in X-Y mode but also containing a sweep circuit. It features differential signal inputs.
There is a similar sister model, the 504, with single-ended inputs. A rack-mount version, the RM503, was also available.
The 503 was $625 in 1960 versus, for example, $1000 for the 516 in 1960.
The 503 features two identical phase matched amplifiers with true differential inputs. The scope has a bandwidth specification of 450 kHz and sensitivity to 1 mV/cm. Due to is its low bandwidth, the 503 can operate at high sensitivities while not responding to interference from broadcast transmitter RF fields, making it suitable for biomedical work.
A large market for the 503 was in electronics labs of educational institutions. The differential inputs are useful for entry level students to experiment with observing voltages not referenced to ground.
Key Specifications
| Bandwidth | DC to 450 kHz (AC coupled 10 Hz) |
|---|---|
| Deflection | 1 mV/div to 20 V/div, 1–2–5, and 2.5:1 variable |
| Inputs | 1 MΩ // 47 pF; max. 350 V (DC + peak AC) |
| CMRR | 100:1 in 1 mV/div to 200 mV/div, 30:1 above (all at ≤50 kHz) |
| Phase | <1° to 450 kHz in 1 mV/div to 200 mV/div (equal X and Y sensitivity, variable in CAL, like polarities, DC coupling); <2° to 50 kHz in 500 mv/div to 20 V/div) |
| Sweep | 1 μs/div to 5 s/div, 1−2−5, variable 2.5:1, magnifier ×2, ×5, ×10, ×20, ×50 |
| Trigger | Internal, 0.5 div from 50 Hz to 50 kHz, increasing to 2 div at 450 kHz; external 0.5 V from 50 Hz to 450 kHz |
| CRT | T5030, 3 kV (no post-deflection acceleration), P2 phosphor standard |
Links
- Tektronix Type 503 Electrical Troubleshooting And Repair by Mr Carlson's Lab @ YouTube
Documents Referencing 503
- (no results)
Internals
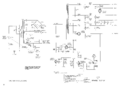
The 503 is mostly a vacuum tube design with a differential transistor stage following the differential input amplifiers.
The power supply design is unique in that unlike other scopes where the high frequency transformer only generates the CRT operating voltages, in the 503 it generates all the operating voltages other than the two filament circuits which are supplied by the AC mains power transformer. It is basically a tube-based (secondary) switch-mode power supply (SMPS). A 6DQ6 power pentode, V620, feeds switched primary current to transformer T620. The switching frequency of V620 is between 25 kHz and 30 kHz, enabling T620 to operate efficiently with much lower core mass than would be required for a transformer operating at mains frequency.
Pictures
-
-
-
-
-
RM503 front panel 1
-
RM503 front panel 2
-
RM503 top view
-
RM503 bottom view 1
-
RM503 bottom view 2
-
RM503 rear panel
-
RM503 with rear panel input connector option
-
503
-
power supply schematic
-
Compensated input attenuator
-
-
503 right side
-
503 left side
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-