565: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Oscilloscope Sidebar | | {{Oscilloscope Sidebar | ||
|manufacturer=Tektronix | |||
image=Rm 565 cal signal.jpg | | |series=560-series scopes | ||
caption=Tektronix RM 565 | | |model=565 | ||
introduced=1962 | | |summary=10 MHz dual-beam scope | ||
discontinued= | |image=Rm 565 cal signal.jpg | ||
|caption=Tektronix RM 565 | |||
manuals= | |introduced=1962 | ||
* [ | |discontinued=1974 | ||
* [ | |manuals= | ||
* [[Media:070-269.pdf|Tektronix 565 Manual]] | |||
* [[Media:Tek 565 preliminary 070-269.pdf|Tektronix 565 Preliminary Manual]] | |||
* [[Media:Tek 565 irb.pdf|Tektronix 565 Instrument Reference Book]] (OCR) | |||
* [[Media:Tek 565 fcp.pdf|Tektronix 564 Factory Calibration Procedure]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tektronix Type 565''' is a [[dual-beam scopes|dual-beam scope]] that takes two [[560-series plug-ins|560-series vertical plug-ins]]. | The '''Tektronix Type 565''' is a [[dual-beam scopes|dual-beam scope]] that takes two [[560-series plug-ins|560-series vertical plug-ins]]. | ||
It was [[introduced in | It was [[introduced in 1962]]. | ||
The 1974 catalog was the last one that included the 565. | The 1974 catalog was the last one that included the 565. | ||
A rackmount version, the RM565, was also produced. Aside from being dual-beam, the 565 is unusual among the | A rackmount version, the RM565, was also produced. Aside from being dual-beam, the 565 is unusual among the other [[560-series scopes]] in the fact that it (the mainframe) has built-in trigger, sweep, and horizontal amplifier circuits. | ||
other [[560-series scopes]] in the fact that it (the mainframe) has built-in trigger, sweep, and horizontal amplifier circuits. | |||
{{BeginSpecs}} | |||
{{Spec|Bandwidth|up to 10 MHz determined by vertical plug-ins}} | |||
{{Spec|Sweep|1 μs/div to 5 s/Div, 1−2−5, ×10 magnifier, and variable }} | |||
{{Spec|Sweep delay| 10 μs to 50 seconds}} | |||
{{Spec|Power|600 W max. including plug-ins}} | |||
Power | {{Spec|Calibrator|1 kHz square wave, 1 mV to 100 V in decade steps}} | ||
{{Spec|CRT| [[T5650]], cathode at −3.9 kV, no post-deflection acceleration}} | |||
{{EndSpecs}} | |||
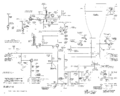
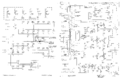
==Circuits== | ==Circuits== | ||
CRT acceleration voltage is produced by a transformer driving a single [[1X2]] rectifier tube. | |||
===Vertical Signal Path=== | ===Vertical Signal Path=== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 37: | ||
The left plug-in bay is for the lower beam and the right plug-in bay is for the upper beam. | The left plug-in bay is for the lower beam and the right plug-in bay is for the upper beam. | ||
A 0. | A 0.7−3 pF trimmer capacitor is connected immediately behind each of the plug-in connectors, and allows | ||
for the mainframe to be calibrated so that plug-ins can be interchanged without requiring the | for the mainframe to be calibrated so that plug-ins can be interchanged without requiring the | ||
high-frequency compensation of the system to be readjusted. | high-frequency compensation of the system to be readjusted. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 45: | ||
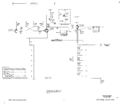
=== Trigger and Sweep === | === Trigger and Sweep === | ||
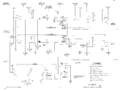
The triggering signal comes from pin 11 on the plug-ins, is amplified by a [[12AT7]]-based cathode follower, | The 565 is the only 560-series mainframe that has built-in trigger, timebase, and horizontal amplifier circuitry. | ||
and sent to "TRIGGER" switches. From there, the trigger signal is sent through a [[6DJ8]]-based differential amplifier | In all other [[560-series scopes]], those functions are performed by the horizontal plug-in. | ||
and then is discriminated by a [[6DJ8]]-based Schmitt trigger. | |||
The triggering signal comes from pin 11 on the plug-ins, is amplified by a [[12AT7]]-based cathode follower, and sent to "TRIGGER" switches. From there, the trigger signal is sent through a [[6DJ8]]-based differential amplifier, and then is discriminated by a [[6DJ8]]-based Schmitt trigger. | |||
The 565 is also unusual in that it employs a [[tunnel diodes|tunnel diode]] (D845, a [[TD4]], which is equivalent to the [[1N3718]]) in the trace intensification circuit. | The 565 is also unusual in that it employs a [[tunnel diodes|tunnel diode]] | ||
(D845, a [[TD4]], which is equivalent to the [[1N3718]]) in the trace intensification circuit. | |||
The tunnel diode forms a bistable multivibrator: kick it one way and it turns on and stays on, | The tunnel diode forms a bistable multivibrator: kick it one way and it turns on and stays on, | ||
kick it the other way and it turns off and stays off. | kick it the other way and it turns off and stays off. | ||
which is a 2N404 germanium PNP transistor. | The tunnel diode is DC-coupled to the base-emitter junction of Q843, | ||
to be germanium. | which is a 2N404 germanium PNP transistor. | ||
Contrast this with the timebase A trigger of the [[585|585A]], which uses a tunnel diode AC-coupled to a transistor, which | Because the tunnel diode and transistor are DC-coupled, the transistor needs to be germanium. | ||
makes the forward voltage of the transistor's base-emitter junction irrelevant. | This is one of the rare cases when a failed germanium transistor cannot be replaced with a silicon part. | ||
Contrast this with the timebase A trigger of the [[585|585A]], which uses a tunnel diode AC-coupled to a transistor, | |||
which makes the forward voltage of the transistor's base-emitter junction irrelevant. | |||
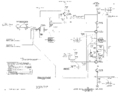
=== Calibrator === | === Calibrator === | ||
| Line 58: | Line 65: | ||
The calibrator is an astable multivibrator formed by one half of a [[12AT7]] and a [[6AU6]]. | The calibrator is an astable multivibrator formed by one half of a [[12AT7]] and a [[6AU6]]. | ||
The other half of the 12AT7 serves as the output cathode follower for the calibrator. | The other half of the 12AT7 serves as the output cathode follower for the calibrator. | ||
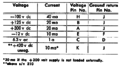
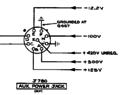
=== Auxiliary Power Jack === | |||
The 565 has an [[Amphenol 165 series connectors|Amphenol 165 series connector]] (J780) on the rear panel, which allows the 565 to provide power to external devices. | |||
The pinout and specs are shown below. | |||
== Comparison with the [[556]] == | == Comparison with the [[556]] == | ||
The 565 appears similar to the [[556]], but is different in many ways. | The 565 appears similar to the [[556]], but is different in many ways. | ||
The 556 uses tunnel diodes for triggering, while the 565 uses tubes. | The 556 uses tunnel diodes for triggering, while the 565 uses tubes. | ||
The 556 uses [[letter-series and 1-series plug-ins]] | The 556 uses [[letter-series and 1-series plug-ins]] while the 565 uses 560-series plug-ins. | ||
Moreover, the bandwidth of the 556 is specified as 50 MHz, while the bandwidth of the 565 is specified as 10 MHz. | Moreover, the bandwidth of the 556 is specified as 50 MHz, while the bandwidth of the 565 is specified as 10 MHz. | ||
Subjectively, the trace of the 565 is very sharp, sharper than the trace of the 556. | Subjectively, the trace of the 565 is very sharp, sharper than the trace of the 556. | ||
== Mechanical == | == Mechanical == | ||
Benchtop (565) and rackmount versions (RM565) were made. | Benchtop (565) and rackmount versions (RM565) were made. | ||
The benchtop version has the following dimensions: | |||
* Width: 17 inches | * Width: 17 inches | ||
* Height: 13.5 inches | * Height: 13.5 inches | ||
| Line 77: | Line 89: | ||
==Pictures== | ==Pictures== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Rm565_1.jpg|Front from RM565 | |||
Rm565_2.jpg | |||
IMG 1213.JPG| Open 565 | |||
Wellenkino 565.jpg | |||
RM565_P7.jpg|RM565 with P7 CRT | |||
Tek 565 block.png|Block Diagram | |||
Tek 565 timebase a timing sw.png|Timebase 'A' Timing Switch | |||
Tek 565 timebase a trig.png|Timebase 'A' Trigger | |||
Tek 565 timebase a gen.png|Timebase 'A' Generator | |||
Tek 565 delay pickoff.png|Delay Pickoff | |||
Tek 565 timebase b trigger.png|Timebase 'B' Trigger | |||
Tek 565 timebase b generator.png|Timebase 'B' Generator | |||
Tek 565 timebase b timing sw.png|Timebase 'B' Timing Switch | |||
Tek 565 horiz display switching.png|Horizontal Display Switching | |||
Tek 565 lower horiz amp.png|Lower Horizontal Amp | |||
Tek 565 crt circuit.png|CRT Circuit | |||
Tek 565 plug-in connectors.png|Plug-in Connectors | |||
Tek 565 heater and power supply.png|Heater Wiring and Power Supply | |||
Tek 565 amplitude calibrator.png|Amplitude Calibrator | |||
Rm 565 front bottom internal.jpg | |||
Rm 565 bottom internal.jpg | |||
Rm 565 cal signal.jpg | |||
Tek565-crop.jpg | Tek565-crop.jpg | ||
Tek rm565 gray1.jpg|Gray RM565 | Tek rm565 gray1.jpg|Gray RM565 | ||
| Line 109: | Line 121: | ||
Tek rm565 gray8.jpg|Gray RM565 | Tek rm565 gray8.jpg|Gray RM565 | ||
Tek rm565 gray9.jpg|Gray RM565 | Tek rm565 gray9.jpg|Gray RM565 | ||
Tek 565 j780.jpg|J780 on rear panel | |||
Tek 565 j780 specs.png|J780 Specs | |||
Tek 565 j780 pinout.png|J780 Pinout | |||
Tek rm565 top inside.jpg | |||
Tek rm565 hvps.jpg | |||
Tek rm565 hv rectifier.jpg | |||
Tek rm565 intensifier circuit.jpg | |||
Rm565 two trace2.jpg | |||
Tek rm565 top internal.jpg|top internal | |||
Tek rm565 right cover off.jpg|LV power supply tubes on the bottom, HV on the top, fan in the rear | |||
Tek rm565 bottom internal.jpg|bottom internal | |||
Tek rm565 rear.jpg|rear | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
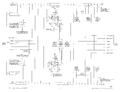
==Components== | |||
{{Parts|565}} | |||
[[Category:560 series scopes]] | [[Category:560 series scopes]] | ||
[[Category:Dual beam scopes]] | [[Category:Dual beam scopes]] | ||
[[Category:Introduced in | [[Category:Introduced in 1962]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:17, 10 March 2024
The Tektronix Type 565 is a dual-beam scope that takes two 560-series vertical plug-ins. It was introduced in 1962. The 1974 catalog was the last one that included the 565.
A rackmount version, the RM565, was also produced. Aside from being dual-beam, the 565 is unusual among the other 560-series scopes in the fact that it (the mainframe) has built-in trigger, sweep, and horizontal amplifier circuits.
Key Specifications
| Bandwidth | up to 10 MHz determined by vertical plug-ins |
|---|---|
| Sweep | 1 μs/div to 5 s/Div, 1−2−5, ×10 magnifier, and variable |
| Sweep delay | 10 μs to 50 seconds |
| Power | 600 W max. including plug-ins |
| Calibrator | 1 kHz square wave, 1 mV to 100 V in decade steps |
| CRT | T5650, cathode at −3.9 kV, no post-deflection acceleration |
Circuits
CRT acceleration voltage is produced by a transformer driving a single 1X2 rectifier tube.
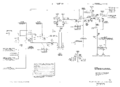
Vertical Signal Path
As is usual for 560-series scopes, the vertical deflection plates of the CRT are driven directly, differentially, by pins 17 and 21 of the vertical plug-in. The left plug-in bay is for the lower beam and the right plug-in bay is for the upper beam.
A 0.7−3 pF trimmer capacitor is connected immediately behind each of the plug-in connectors, and allows for the mainframe to be calibrated so that plug-ins can be interchanged without requiring the high-frequency compensation of the system to be readjusted. The capacitance seen by the plug-in driving the scope should be 14.3 pF for either beam.
There is no trigger pickoff in the vertical signal path of the 565. That function is performed by the plug-ins.
Trigger and Sweep
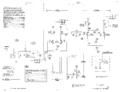
The 565 is the only 560-series mainframe that has built-in trigger, timebase, and horizontal amplifier circuitry. In all other 560-series scopes, those functions are performed by the horizontal plug-in.
The triggering signal comes from pin 11 on the plug-ins, is amplified by a 12AT7-based cathode follower, and sent to "TRIGGER" switches. From there, the trigger signal is sent through a 6DJ8-based differential amplifier, and then is discriminated by a 6DJ8-based Schmitt trigger.
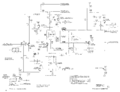
The 565 is also unusual in that it employs a tunnel diode (D845, a TD4, which is equivalent to the 1N3718) in the trace intensification circuit. The tunnel diode forms a bistable multivibrator: kick it one way and it turns on and stays on, kick it the other way and it turns off and stays off. The tunnel diode is DC-coupled to the base-emitter junction of Q843, which is a 2N404 germanium PNP transistor. Because the tunnel diode and transistor are DC-coupled, the transistor needs to be germanium. This is one of the rare cases when a failed germanium transistor cannot be replaced with a silicon part. Contrast this with the timebase A trigger of the 585A, which uses a tunnel diode AC-coupled to a transistor, which makes the forward voltage of the transistor's base-emitter junction irrelevant.
Calibrator
The calibrator is an astable multivibrator formed by one half of a 12AT7 and a 6AU6. The other half of the 12AT7 serves as the output cathode follower for the calibrator.
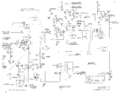
Auxiliary Power Jack
The 565 has an Amphenol 165 series connector (J780) on the rear panel, which allows the 565 to provide power to external devices. The pinout and specs are shown below.
Comparison with the 556
The 565 appears similar to the 556, but is different in many ways. The 556 uses tunnel diodes for triggering, while the 565 uses tubes. The 556 uses letter-series and 1-series plug-ins while the 565 uses 560-series plug-ins. Moreover, the bandwidth of the 556 is specified as 50 MHz, while the bandwidth of the 565 is specified as 10 MHz. Subjectively, the trace of the 565 is very sharp, sharper than the trace of the 556.
Mechanical
Benchtop (565) and rackmount versions (RM565) were made. The benchtop version has the following dimensions:
- Width: 17 inches
- Height: 13.5 inches
- Depth: 23.375 inches
- Weight: 67 pounds
The RM565 weighs 80 pounds.
Pictures
-
Front from RM565
-
-
Open 565
-
-
RM565 with P7 CRT
-
Block Diagram
-
Timebase 'A' Timing Switch
-
Timebase 'A' Trigger
-
Timebase 'A' Generator
-
Delay Pickoff
-
Timebase 'B' Trigger
-
Timebase 'B' Generator
-
Timebase 'B' Timing Switch
-
Horizontal Display Switching
-
Lower Horizontal Amp
-
CRT Circuit
-
Plug-in Connectors
-
Heater Wiring and Power Supply
-
Amplitude Calibrator
-
-
-
-
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
Gray RM565
-
J780 on rear panel
-
J780 Specs
-
J780 Pinout
-
-
-
-
-
-
top internal
-
LV power supply tubes on the bottom, HV on the top, fan in the rear
-
bottom internal
-
rear
Components
Some Parts Used in the 565
| Part | Part Number(s) | Class | Description | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0G3 | 154-0291-00 | Gas Discharge Tube (Voltage regulator) | 85 V voltage reference | 132 • 506 • 547 • 560 • 561 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 • 567 • 661 • TU-4 • Z • Keithley 610 |
| 120-289 | 120-289 | Discrete component | transformer | 565 |
| 12AT7 | 154-0039-00 | Vacuum Tube (Dual Triode) | dual high-gain triode | 161 • 180 • 310 • 310A • 315 • 316 • 360 • 502 • 502A • 511A • 512 • 513 • 513D • 514 • 514AD • 514D • 516 • 524 • 529 • RM529 • 544 • 546 • 547 • 556 • 565 • 570 • 3A2 • 75 • 3A75 • 1M1 • A • B • C • G • H • K • L • ML • M • N • K • R • S • Z • Keithley 610B |
| 1X2 | 154-0005-00 | Vacuum Tube (Diode) | high-voltage rectifier | 420 • 507 • 565 |
| 6080 | 154-0056-00 • 154-0315-00 | Vacuum Tube (Dual Triode) | dual power triode | 132 • 160 • 316 • 317 • 516 • 535 • 535A • RM35A • 541 • 541A • 535 • 536 • 545 • 545A • 545B • 546 • 547 • 549 • 565 • 567 • 575 • 581 • 581A • 585 • 585A |
| 6AL5 | 154-016 • 154-0016-00 • 154-0038-00 | Vacuum Tube (Dual Diode) | high-perveance dual diode | 163 • 181 • 190 • 1M1 • 310 • 310A • 315 • 316 • 317 • 3B1 • 3B1S • 3B2 • 3B3 • 3B5 • 502 • 502A • 503 • 511 • 511A • 512 • 516 • 517 • 517A • 524 • 526 • 535 • 535A • 545 • 545A • 549 • 551 • 565 • 570 • 581 • 581A • 585 • 585A • C • T • Telequipment D52 • Telequipment D56 • Telequipment S52 |
| 6AN8 | 154-078 • 154-0078-00 | Vacuum Tube (Triode/Pentode) | triode-pentode combo | 310 • 310A • 316 • 317 • 360 • 502 • 502A • 516 • 517 • 517A • 526 • 565 • 570 • 575 • N |
| 6AU6 | 154-0022-00 • 157-0073-00 • 157-0059-00 • 154-0284-00 | Vacuum Tube (Pentode) | RF pentode | 107 • 160 • 181 • 190 • 60 • 2A60 • 72 • 3A72 • 3C66 • 310 • 310A • 316 • 317 • 360 • 502 • 502A • 506 • 511 • 511A • 512 • 513 • 516 • 517 • 517A • 524 • 526 • 529 • RM529 • 531 • 531A • 535 • 536 • 545 • 545A • 546 • 547 • 549 • 555 • 561 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 • 567 • 570 • 575 • 581 • 581A • 585 • 585A • 80 • C • CA • Q |
| 6BC7 | 154-0232-00 | Vacuum Tube (Diode) | triple diode | 503 • 504 • 565 • 67 • 2B67 |
| 6BJ7 | 154-0453-00 | Vacuum Tube (Diode) | triple diode | 503 • 526 • 565 |
| 6BL8 | 154-0278-00 | Vacuum Tube (Triode/Pentode) | triode-pentode combo | 67 • 2B67 • 3B1 • 3B1S • 3B2 • 3B3 • 3B4 • 503 • 504 • 506 • 516 • 549 • 561 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 • 567 • Telequipment D52 • Telequipment D56 • Telequipment S31 • Telequipment S32 • Telequipment S32A • Telequipment S51 • Telequipment S52 |
| 6CW4 | 154-0323-00 | Vacuum Tube (Triode) | Nuvistor triode | 1A7 • 3A8 • 3B2 • 3S76 • 6R1 • 565 • S-311 |
| 6CZ5 | 154-0167-00 | Vacuum Tube (Pentode) | power pentode | 317 • 502 • 506 • 526 • 555 • 561 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 • 567 |
| 6DJ8 | 154-0187-00 • 154-0305-00 | Vacuum Tube (Dual Triode) | dual triode | 067-506 • 111 • 132 • 161 • 310A • 316 • 317 • 502 • 502A • 503 • 504 • 506 • 515 • 516 • 519 • 526 • 529 • RM529 • 533 • 535 • 536 • 543 • 544 • 545 • 545A • 545B • 546 • 547 • 549 • 555 • 556 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 • 567 • 581 • 581A • 585 • 585A • 661 • 1A4 • 1S1 • 60 • 2A60 • 63 • 2A63 • 67 • 2B67 • 3A1 • 3A1S • 3A2 • 3A3 • 3A6 • 3A7 • 72 • 3A72 • 75 • 3A75 • 4S2 • 51 • 3B1 • 3B1S • 3B2 • 3B3 • 3B4 • 3M1 • 3S76 • 3T77 • 3T77A • 9A1 • 9A2 • 1121 • 80 • 81 • 82 • 86 • B • O • W • Z • Telequipment D56 • Telequipment S32A • Telequipment D52 • S-311 • Telequipment TD51 • Telequipment S52 • Telequipment S51 • Telequipment Type A • TU-4 |
| 7233 | 154-307 • 154-0307-00 | Vacuum Tube (Triode) | low-mu triode | 132 • 506 • 561 • 561A • 561S • 564 • 565 |
| RT5204 | 151-0058-00 | Discrete component | Silicon NPN transistor | 565 • RM565 • Z • 2A61 • 3B1 • 3B3 • 3S76 • 3T77 |
| STD916 | 152-0098-00 | Discrete component | 10 mA, 90 pF tunnel diode | 556 • 565 • RM565 • 661 |
| T5650 | 154-0357-00 • 154-0358-00 • 154-0359-00 • 154-0360-00 • 154-0368-00 • 154-0426-00 • 154-0439-00 • 154-0440-00 • 154-0441-00 • 154-0477-00 • 154-0477-01 • 154-0477-02 • 154-0477-03 | CRT | dual-beam CRT | 565 |