7912: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
'''7912AD/HB''' | '''7912AD/HB''' | ||
* [[Media:7912ad_theory.pdf | 7912AD Operator's Manual (partial, 57 pages from introduction)]] | * [[Media:7912ad_theory.pdf | 7912AD Operator's Manual (partial, 57 pages from introduction)]] | ||
* [ | * [[Media:7912ad reading gun supply.pdf|7912AD Video preamp/Reading gun supply schematics]] | ||
* [ | * [[Media:7912ad writing gun supply.pdf|7912AD Z-Axis/HV board schematics]] | ||
* [[Media:070-5077-00.pdf|Tektronix 7912AD Instrument Interfacing Guide]] | * [[Media:070-5077-00.pdf|Tektronix 7912AD Instrument Interfacing Guide]] | ||
* [[Media:47W-5355.pdf|Tektronix 7912AD Brochure]] | * [[Media:47W-5355.pdf|Tektronix 7912AD Brochure]] | ||
Revision as of 04:52, 10 December 2023
The Tektronix 7912 is a series of high-speed digitizers that take one 7000-series vertical plug-in and one 7000-series horizontal plug-in.
All 7912 models use the same internal CRT-based, digitizing scan converter tube (T7912, 154-0698-00) that is not visible from the outside. The signal from the vertical plug-in deflects a writing beam through distributed deflection plates. The electrons hit a small flat rectangular solid state target, conceptually similar to the image sensor in a digital camera. The resolution of the target is 512×512, giving 512 points in the time domain and 9-bit linear quantization of the input voltage.
With a 7B92 sweeping the whole X-axis in 5 ns, and the 7912 capturing 512 samples in that sweep, the 7912 performs the function of a 100 GSample/s A/D converter.
The primary markets for the 7912 series were nuclear and laser research.
7912 project staff:
- Carlo Infante, Program manager
- Jim Cavoretto, Project Engineer
- Al Allworth, Don Roberts, and Stu McNaughton, Electrical Engineers
- Walt Lowy, Engineering Technician
- Ray Hayes, Ken Hawken, Bob Culter, Hal Cobb, Ed Ritz, and Bo Janko, CRT Engineering
- Loyal Strom, Helene Albright and Ken Nesvold, Prototype Support
- Doug Giesbers, Larry Pearson and Phil Lloyd, Mechanical Engineering
- Nick Hughes and Ray Blohm, Instrument Manufacturing
R7912
The R7912, introduced in September 1973 (Ref.1), achieved a bandwidth of 500 MHz with a 7A19 vertical amplifier plug-in. It was also possible, like in the 7904 scope, to access the CRT deflection plates directly through a 7A21N plug-in and achieve a bandwidth of 1 GHz, albeit at reduced sensitivity (4 V/Div) and loss of triggering and readout functions. Some customers further modified the stock 7912 to increase bandwidth up to 3 GHz in special applications (see literature links below).
The reading beam operates differently depending on the output mode. In TV mode, the reading beam scans the target in a horizontal format similar to that used in conventional television systems, and a video output compatible with TV monitors is generated. In Digital mode, the reading beam scans the target vertically, in 512 discrete steps for each of 512 horizontal positions. Waveforms are converted to digital, stored in memory, and can be read by a computer.
The R7912 used the 7000 series readout system writing readout characters onto the storage target, which would become part of the output signal in the NON STORE mode.
The R7912 had a proprietary digital interface. A card for interfacing to a DEC PDP-11 was available. The Tektronix 067-0679-00 aka 1350 "Digital Display Controller" or "Memory Display Unit" is an external module that interfaces the R7912 to X-Y monitors. Tek also offered configurations with multiple R7912s on a common controller within the WP2000 series.
7912AD and 7912HB
From the 7912AD (1978) on, the instrument had a standard GPIB interface and could drive X-Y monitors directly. In contrast to the earlier R7912, the readout characters in video mode were created digitally and directly injected into the video signal. The 7912AD has 500 MHz bandwidth. It was succeeded by the 750 MHz 7912HB in 1987 (using a 7A29P amplifier).
For the 7912AD and 7912HB, special GPIB-controllable plug-in modules with a 'P' (Programmable) suffix were available, e.g. 7A16P, 7A29P and 7B90P.
7912AD Options
- Option 4: Change to fast digitize mode. This option trades off scan time with resolution by compressing the scan. The target is written on and read from a 256 x 256 point matrix with a maximum of 14 points stored per vertical scan. This option is achieved by setting the correct jumpers on the A16, A20, A22, A26, A46 boards.
- Option 13: Changes the video output to 625 lines/frame with a 50 Hz field rate (PAL). This option is achieved by setting the correct jumpers on the A20 and A28 boards.
Internals
Three output methods are provided: Video (NTSC or PAL), X-Y-Z low-speed analog, and a GPIB interface. For video-out, Tektronix recommended the 634 monitor or a monitor from the 650- and 670-series and a 75 Ω termination. For X-Y-Z analog, Tek recommended a 600-series monitor and no specific termination requirement.
With aftermarket modifications to the electronics, 7912AD bandwidths have been extended up to 3 GHz in special cases.
Specifications
The Tektronix 7912AD is 19" wide, 7" tall, 27" deep, and weighs 55 pounds. It consumes 360 watts maximum.
Literature and Software
- Hale Farley, The introduction of the R7912 in Tek Retirees Newsletter 11/2012
- US Patent 3748585: Silicon Diode Array Scan Converter Tube and Method of Operation. Culter et al, July 1973.
- LLE Review, Oct-Dec 1985 mentioning the LM7912A, a Lockheed-modified R7912 variant having "a bandwidth of 3.5 GHz at the -3 dB point, less than 5% undershoot and overshoot, with a 12-bit output (2 mV/bit)"
- Lockheed Palo Alto Research Lab study for LLL (June 1978) describing the LM7912 Enhanced Performance Transient Digitizer, claiming 3 GHz bandwidth
- William B. Boyer, Data Acquisition and Processing on Electron Beam Fusion Accelerators. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science Vol.NS-25, No. 1, February 1978
- Thesis on "7912ADM" upgrade version, Jonathan B. Scott
- Improvement of the Bandwidth of the Transient Digitizers in the LIDAR Thomson Scattering Diagnostic on JET. Risø National Laboratory, Denmark, June 1990 discussing how removing the delay line and replacing the compensation circuit can boost the 7912AD+7A29 combination to 1.1 GHz bandwidth
- 7912 GPIB examples
Links
Documents Referencing R7912
| Document | Class | Title | Authors | Year | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekscope 1973 V5 N6 Nov 1973.pdf | Article | Digitizing and displaying fast pulses | Hale Farley | 1973 | R7912 |
| Tekscope 1973 V5 N6 Nov 1973.pdf | Article | A New Way to Look At Transients | Carlo Infante | 1973 | R7912 |
| Data Acquisition and Processing on Electron Beam Fusion Accelerators - William Boyer 1978.pdf | Article | DATA ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING ON ELECTRON BEAM FUSION ACCELERATORS | William B. Boyer | 1978 | R7912 • 4010 • 4610 • 4631 • 1340 |
| Lockheed report-lmsc-d628276.pdf | Article | Enhanced Performance Transient Digitizer, the LM7912 | 1978 | LM7912 • R7912 | |
| Tek retiree news 2012 11 nov.pdf | Article | Tektronix R7912 Programmable Transient Waveform Digitizer | Hale Farley | 2012 | R7912 |
Documents Referencing 7912AD
| Document | Class | Title | Authors | Year | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekscope 1979 V11 N1.pdf | Article | An Intelligent, Programmable Transient Digitizer | Dale Aufrecht | 1979 | 7912AD • 7A16P • 7B90P |
| RISOM2873.pdf | Article | Improvement of the Bandwidth of the Transient Digitizers in the LIDAR Thomson Scattering Diagnostic on JET | Erik Kristensen | 1990 | 7912AD • 7A29 • 7704A • 7S12 • S-6 • S-52 |
See Also
- WP2051, WP2052
- MP1101
- SCD1000, SCD5000
- 670-6466-00 7912 AD plug-in interface extender
- 067-0854-00 Calibration Kit
- 067-0679-99 R7912 Demo Unit
Pictures
R7912
-
R7912 connected to a modern video monitor. Note 7000-style readout.
-
R7912 front
-
R7912 controls
-
R7912 rear
-
067-0679-00 front next to 608 monitor
-
067-0679-00 rear next to 608 monitor
-
067-0679-00 detail
-
067-0679-00 aka 1350
7912AD
-
7912AD front
-
7912AD front
-
7912AD front
-
7912AD rear
-
7912AD top view, cover removed
-
7912AD top view, cover removed
-
7912AD top detail with A34 vertical amp
-
7912AD right
-
7912AD bottom, cover removed
-
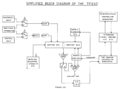
7912AD block diagram
-
7912AD digitizer tube
-
T7912 tube - read part (left), target (center), write part (right). See T7912 article for more photos.
-
7912AD TV output on NTSC monitor
-
7912AD Back side of front panel
-
7912AD A10 rear
-
7912AD A10 front with buttons partially removed to access the 150-0048-01 lamps
-
7912AD A12 power button PCB front
-
7912AD A12 power button disassembled to access the 150-0048-01 lamp
-
7912AD A12 power button PCB rear
-
7912AD A16 Memory Control with 82S185 PROMs
-
7912AD A18 Data Memory
-
7912AD A18 Data Memory with IM5610 PROMs
-
7912AD A20 data buffer
-
7912AD A20 data buffer
-
7912AD A22 translator
-
7912AD A22 translator
-
7912AD A24 graticule generator
-
7912AD A24 graticule generator
-
7912AD A26 X-Y ramp generator
-
7912AD A26 X-Y ramp generator
-
7912AD A28 video processor
-
7912AD A32 Video preamp
-
7912AD A40 horizontal
-
7912AD A38 scan amplifier
-
7912AD A54 MPU (new version with 6802 CPU SN B111166up)
-
7912AD A54 MPU (new version with 6802 CPU SN B111166up)
-
7912AD A56 IEEE 488
-
7912AD A56 IEEE 488
-
7912AD A62 power connector PCB
-
7912AD A62 power connector PCB
-
670-6466-00 plug-in extender
7912HB
-
7912HB
-
7912HB
-
7912HB
-
7912HB
Components
Some Parts Used in the R7912
Some Parts Used in the 7912AD
Some Parts Used in the 7912HB